Spanning Tree and the Bridged Network
5-7
Figure 5-3
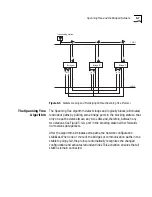
Packets Looping and Multiplying Without Spanning Tree Protocol
The Spanning Tree
Algorithm
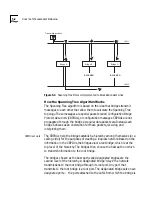
The Spanning Tree algorithm detects loops and logically blocks (eliminates)
redundant paths by putting some bridge ports in the blocking state so that
only one path exists between any two LANs and, therefore, between any
two stations. See Figure 5-4. A port in the blocking state neither forwards
nor receives data packets.
After the algorithm eliminates extra paths, the network configuration
stabilizes. When one or more of the bridges or communication paths in the
stable topology fail, the protocol automatically recognizes the changed
configuration and activates redundant links. This activation ensures that all
stations remain connected.
Transmitting station
LAN 1
LAN 2
Bridge C
1
1
1
1b
1c
1a
1a
Bridge A
1b
1c
Bridge B
Содержание LANPLEX 2500
Страница 1: ...LANPLEX 2500 OPERATION GUIDE Part No 801 00344 000 Published November 1996 Revision 03...
Страница 14: ......
Страница 18: ...1 4 CHAPTER 1 LANPLEX MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION OVERVIEW...
Страница 78: ...III Chapter 9 FDDI Overview and Implementation Chapter 10 FDDI Networks FDDI TECHNOLOGY...
Страница 97: ...IV Chapter 11 ATM Networks ATM TECHNOLOGY...
Страница 116: ...V Appendix A SNMP MIB Support Appendix B Technical Support APPENDIXES...