1-8
TI 77C01H01-01EN
Oct. 17, 2018-00
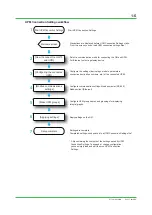
6. Power monitor wiring precautions
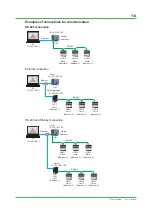
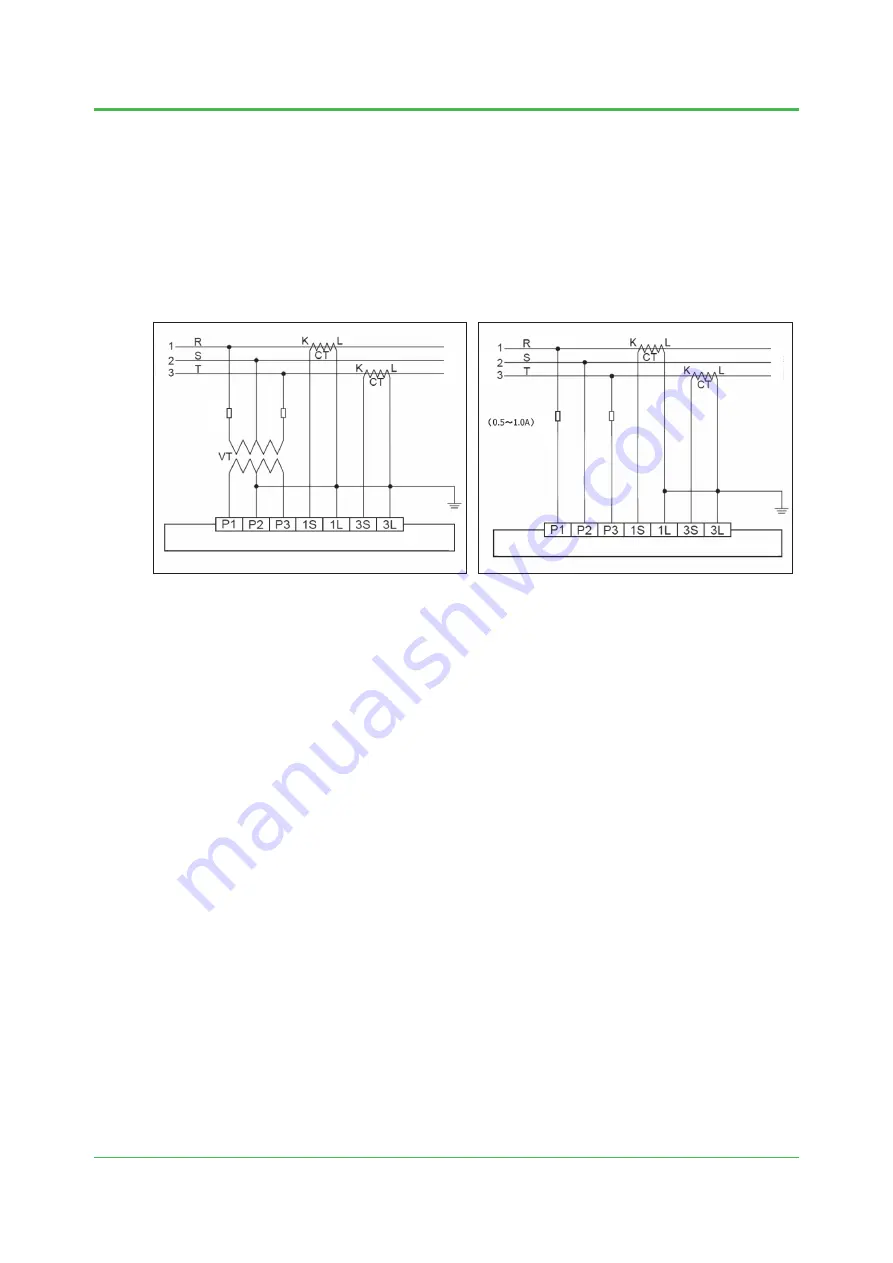
UPM100 Power Monitor wiring example
Wiring without a VT (3 phase 3 wire example)
Note: If not using a VT, do not ground P2.
With a VT
Without a VT
Power supply
Power supply
Load
Fuse
Fuse
Load
This is an example with the UPM100, but the voltage input wiring is also the same on the PR300
and UPM101.
Selecting a fuse
If not using a VT, insert a fuse of 0.5–1.0 A into lines P1 and P3.
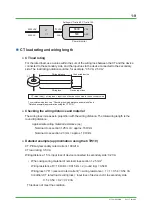
Setting the VT and CT ratios
What are the VT and CT ratios?
Generally, when measuring high voltage and high current transformer signals, you use a VT
(voltage transformer) and CT (current transformer). The ratio between the primary and secondary
voltage and current ratings are the VT and CT ratios. With these ratios, a power monitor can
convert the primary voltage and current of the VT and CT and display the electrical quantities.
VT ratio: VT primary/secondary voltage rating
Ex.: VT ratio = 6600 VAC/110 VAC = 60
CT ratio: CT primary/secondary current rating
Ex.: CT ratio = 500 AAC/5 AAC = 100
If not using a VT or CT, each ratio is 1.