<9. Maintenance>
9-1
IM 01C27C01-01EN
9. Maintenance
9.1 Overview
WARNING
Since the accumulated process fluid may be
toxic or otherwise harmful, take appropriate care
to avoid contact with the body or inhalation of
vapors when draining condensate or venting gas
from the transmitter pressure-detector section
and even after dismounting the instrument from
the process line for maintenance.
Maintenance of the transmitter is easy due to its
modular construction. This chapter describes the
procedures for calibration, adjustment, and the
disassembly and reassembly procedures required
for component replacement.
Transmitters are precision instruments. Please
carefully and thoroughly read the following sections
for information on how to properly handle them
while performing maintenance.
IMPORTANT
• As a rule, maintenance of this transmitter
should be done in a maintenance room that
has all the necessary tools.
• The CPU assembly, RF assembly, and
Integral indicator contain sensitive parts that
can be damaged by static electricity.
Take precautions such as using a grounded
wrist strap when handling electronic parts or
touching the board circuit patterns. Also be
sure to place the removed CPU assembly,
RF assembly, or Integral indicator into a bag
with an antistatic coating.
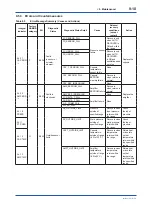
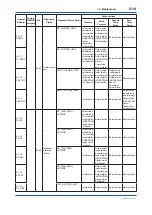
9.2 Calibration Instruments
Selection
Table 9.1 lists the instruments that can be used
to calibrate a transmitter. When selecting an
instrument, consider the required accuracy level.
Exercise care when handling these instruments to
ensure they maintain the specified accuracy.
9.3 Calibration
Use the procedure below to check instrument
operation and accuracy during periodic
maintenance or troubleshooting.
1) Insert the battery pack or turn on the power
and then perform provisioning to have the
transmitter join the Field Wireless Network
or preparing the infrared communication for
calibration.
2) Set measurement mode to continuous using
the field device configuration tool and the
update period to 1 second using the field
wireless configuration tool.
3) Connect the devices as shown in Figure 9.1
and allow the transmitter to warm up for at least
5 minutes.
IMPORTANT
If the measurement range 0% point is 0 kPa
or shifted in the positive direction (suppressed
zero), the reference pressure should be applied
as shown in the figure.
If the measurement range 0% point is shifted
in the negative direction (elevated zero), the
reference pressure should be applied using a
vacuum pump.
4) Apply reference pressures of 0%, 50%,
and 100% of the measurement range to the
transmitter. Calculate the errors (differences
between the device configuration tool readings
and reference pressures) as the pressure is
increased from 0% to 100% and is decreased
from 100% to 0%, and confirm that the errors
are within the required accuracy.
(Note) When the output mode is set to “Sg root,” apply reference
pressures of 0, 6.25, 25, 56.25, and 100% instead.
5) When the test is finished, reset measurement
mode and update time to the initial value using
the field device configuration tool and the field
wireless configuration tool.