Check
Explanation/Comment
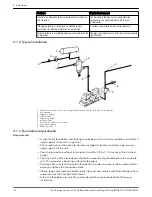
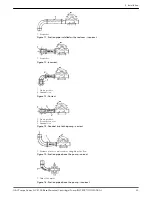
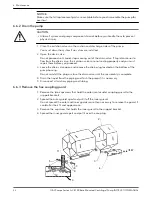
Always run piping to the pump.
Do not move pump to pipe. This could make final
alignment impossible.
Check that the suction and discharge piping are
supported independently near the pump and properly
aligned.
This helps to avoid strain on the pump when the flange
bolts are tightened.
Check that pipe hangers or other supports are installed.
Place supports at necessary intervals.
Check if expansion joints are installed correctly.
When expansion joints are used in the piping system,
they must be installed beyond the piping supports
closest to the pump. Tie bolts should be used with
expansion joints to prevent pipe strain. Do not install
expansion joints next to the pump or in any way that
would cause a strain on the pump resulting in system
pressure changes.
Check that pipe size is larger at pump connections.
It is usually advisable to increase the size of both suction
and discharge pipes at the pump connection to decrease
the loss of head from friction.
Install piping as straight as possible to avoid unnecessary
bends.
Use 45 degree or long sweep 90 degree fitting to
decrease friction losses.
Make sure that all piping joints are air tight.
Where flanged joints are used, assure that inside
diameters match properly.
Do not “spring” piping when making any connections.
Provide for pipe expansion when hot fluids are to be
pumped.
4.3.2 Suction piping checklist
The sizing and installation of the suction piping is extremely important. It must be selected
and installed so that pressure losses are minimized and sufficient liquid flows into the
pump when it is started and operated. Many NPSH problems can be directly attributed to
improper suction piping systems.
Piping checklist
Check
Explanation/comment
Checked
Keep the suction piping short in length, as
direct as possible, and never smaller in
diameter than the pump suction opening.
If the suction pipe is short, the pipe diameter can be
the same size as the suction opening. If longer suction
piping is required, pipes should be one or two sizes
larger than the opening depending on piping length.
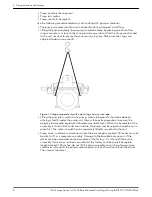
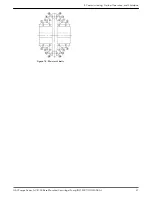
Check that the elbows in the suction piping
for horizontal double-suction pumps are
installed per the Hydraulics Institute
Standards since there is always an uneven
turbulent flow around an elbow.
When there is an elbow in a position other than the
vertical when in relation to the pump suction nozzle,
this causes more liquid to enter one side of the
impeller than the other. The result is highly
unequalized thrust loads that overheat the bearings
and cause rapid wear, which adversely affects the
hydraulic performance. See the Example of
unbalanced loading figure.
Check that pipe reducers on the inlet side
have no more than one pipe diameter
reduction in a single reducer.
This avoids excessive turbulence and noise.
When operating on a suction lift, check that
the suction pipe slopes upward to the
pump nozzle.
A horizontal suction line must have a gradual rise to
the pump. Any high point in the pipe can become
filled with air and prevent proper operation of the
pump.
4 Installation
G&L Pumps Series A-C 8100 Base Mounted Centrifugal Pump INSTRUCTION MANUAL
21