XVME-200/290 Manual
December, 1987
2.4.3
Interrupt Level Selection Jumpers
The DIO Module can either be configured to generate VMEbus interrupts at levels
1-7 or the module interrupt capability can be completely disabled. Table 2-4 shows
how jumpers JAI-JA3 are used to determine the interrupt level status for the DIO
Module.
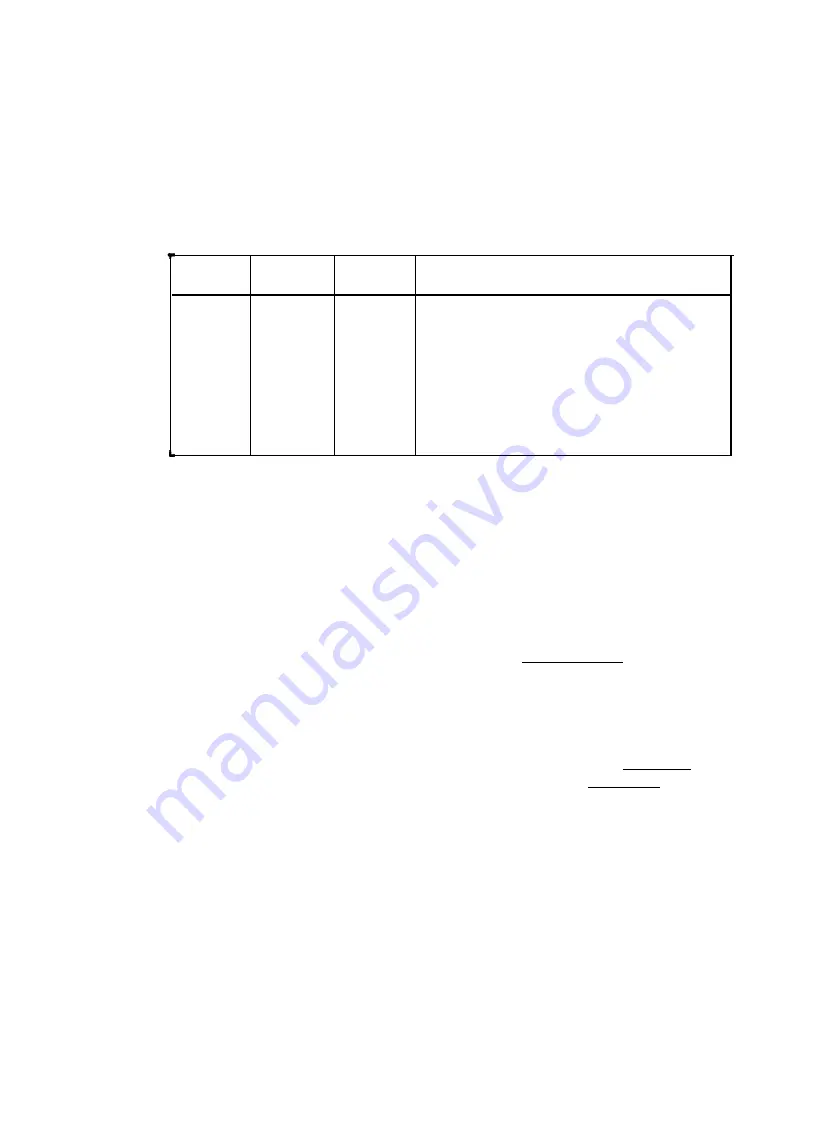
Table 2-4. Interrupt Level Jumper Positions
JA3
In
In
In
In
Out
Out
Out
Out
JA2
In
In
Out
Out
In
In
Out
Out
JAl
In
Out
I N
Out
In
Out
In
Out
Interrupt Level Selected
None, VMEbus Interrupter disabled
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Level 4
Level 5
Level 6
Level 7
The modules are shipped from the factory with jumpers JAI, JA2, and JA3 installed.
NOTE
When the module is never required to generate interrupts,
JAl, JA2, and JA3 should all be installed to ensure that a
programming bug will not generate a VMEbus interrupt.
2.4.4
BGIN*/BGOUT*-IACKIN*/IACKOUT*
Daisy Chain
The Data Bus Arbitration signals BGIN*/BGOUT* are not used by the DIO Module
and are hardwired together on the module to allow the Bus Arbitration Daisy Chain
to pass through the backplane slot occupied by the DIO Module. In each slot of
the VMEbus backplane there are set of jumpers which short the “IN” lines to the
“OUT” lines. Since the BGIN*/BGOUT* signals are already hardwired on the DIO
Module, it is not necessary to insert the corresponding jumper on the slot occupied
by the DIO Module. However, the IACKIN*/IACKOUT* signals are used by the DIO
Module and thus, the backplane jumper for these signals must not be installed in
the backplane slot occupied by the DIO Module.
2.4.5
Handshake Line H2 Direction Jumpers
The 68230 PI/T chips on the DIO Module can be programmed to operate in Modes 0
and 1 (refer to the 68230 Manual for mode explanation).
Data transfers in these
modes can be controlled via the four handshake pins on each chip.
These
handshake pins are designed to be used in any of several different programmable
protocols (a thorough understanding of Modes 0 and 1, and their associated
submodes presented in the 68230 Manual is necessary in order to fully understand
the variety of protocols).
2-8
Summary of Contents for XVME 200
Page 1: ......
Page 2: ......
Page 3: ......
Page 4: ......
Page 7: ......
Page 8: ......
Page 14: ......
Page 15: ......
Page 16: ......
Page 23: ......
Page 31: ......
Page 49: ......
Page 50: ......
Page 51: ......
Page 52: ......
Page 53: ......
Page 54: ......
Page 55: ......
Page 56: ......
Page 57: ......
















































