28
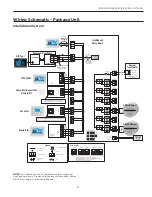
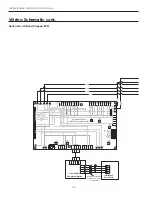
INTELLIZONE2 SPECIFICATION CATALOG
Peak Heating and Cooling Demands
Cooling-Dominated Structures
In cooling-dominated structures such as commercial
buildings and southern residential homes (where electric
heat is rarely needed as an auxiliary heat source), up to
five load calculations need to be performed. Commercial
hourly peak load calculations on all of the four zones
under control of the IntelliZone2 System are required. This
information sizes the supply air ductwork and the zone
damper properly. The fifth load is the entire building (all four
zones). Why perform this step? Because the different zones
have different times of day when they need peak cooling or
heating. The actual peak cooling or heating load is usually
less than the sum of the peak loads for the four zones.
The load calculation for the entire structure is used to size
the HVAC equipment only. Ductwork branches and zone
dampers are sized using the peak zone conditions for each
particular zone. The difference between the sum of the
peak loads for the individual zones and the peak load for
the entire building is called “diversity”.
Diversity is a measurement of the effective cooling or
heating capacity added to the system due to zoning. The
physical heating or cooling capacity is not increased,
but because it is more effective, HVAC equipment can
be sized smaller using zoning diversity. This represents
the first cost savings of the IntelliZone2 Comfort Zoning
System. Secondary savings are attributed to the lower
operating costs.
Many popular software packages or HVAC residential
loads now calculate peak zone loads; check your software
package for its capability.
Heating-Dominated Structures
In heating-dominated structures, such as northern
residential homes (where units are generally sized with
a small amount of electric heat installed as an auxiliary
heat source), diversity may be present in cooling; however,
the unit size is dictated by the heating load and diversity
is rarely present. In this application, a simple room-by-
room or zone-by-zone analysis can be performed with the
resultant sum of the rooms or zones taken as the whole
house load. The table below lists the four zone loads of this
example home.
NOTE:
Dual Capacity 5 Series has a 70% low capacity
output, therefore minimum cfm required per zone is 40% of
nominal cfm.
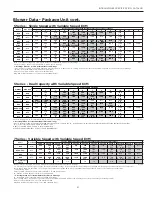
Example Four Zone Load Summary
Htg
Btu/h
Htg
cfm
Total
Clg
Sens
Clg
Clg
cfm
Max
cfm
Adjusted
100% cfm
Min cfm
Req’d.
Design
cfm
# of
Branch
Actual
cfm %
Actual
Load %
Zone
DIP %
Zone 1 Main Living
Kitchen
2259
73
3128
2400
145
145
118
1
Family
4264
138
6660
5128
311
311
252
2
Utility
3002
97
1614
1243
75
97
78
1
Living/Dining
6351
205
7158
5511
334
334
271
3
Total
15876
512
18560
14282
866
887
718
600
718
29%
34%
45%
Zone 2 Bedrooms
Bdrm
1
3224
104
1939
1752
106
106
240
2
Main
Bath
892
29
284
407
25
65
147
1
Bdrm
2
2708
87
1692
1550
94
94
213
1
Total
6824
220
3915
3709
225
265
215
600
600
24%
15%
45%
Zone 3 Master Suite
Mstr
Bdrm
2806
91
2294
1766
107
107
351
2
Mstr
Bath
2350
76
1504
1158
70
76
249
1
Total
5156
166
3798
2924
177
183
148
600
600
24%
11%
45%
Zone 4 Basement
Total
19123
617
5007
3967
240
517
419
600
600
4
24%
41%
45%
Total Zones
46979
1515
31280
24882
1508
1852
1500
2518
Total House
46290
@ 70°F
32822
@ 20°F
123%
100%
168%
Unit Data
Nom Hi cfm
Min Lo cfm
40% Nom cfm
Model
ND*049
1500
1350
600