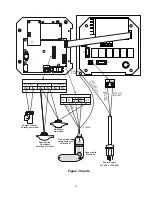
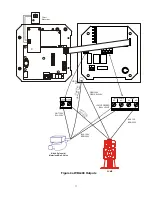
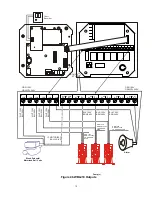
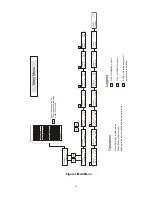
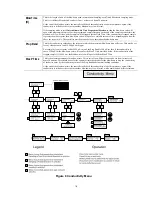
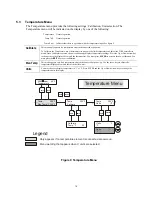
5
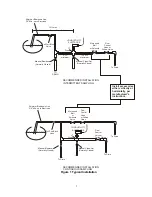
6. There MUST be a flow restriction after the electrode and/or control valve in order to provide
back pressure. This flow restriction will be either a flow control valve or an orifice union. The
amount of the flow restriction will affect the blowdown rate as well, and should be sized
accordingly.
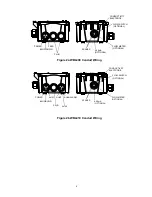
7. Install the motorized ball valve or solenoid valve per the manufacturer’s instructions.
8. For best results, align the hole in the conductivity electrode such that the direction of water flow
is through the hole.
Guide to Sizing Blowdown Valves and Orifice Plates
1. Determine the Rate of Steam Production in Pounds per Hour:
Either read off the boiler name plate (water-tube boilers) or
Calculate from horsepower rating (fire-tube boilers):
HP x 34.5 = lbs/hr.
Example: 100 HP = 3450 lbs/hr.
2. Determine the Concentration Ratio (BASED ON FEEDWATER)
A water treatment chemical specialist should determine the desired number of cycles of concentration.
This is the ratio of TDS in the boiler water to TDS in the feedwater. Note that feedwater means the water
that is fed to the boiler from the deaerator and includes makeup water plus condensate return.
Example: 10 cycles of concentration has been recommended
3. Determine the Required Blowdown Rate in Pounds Per Hour
Blowdown Rate = Steam Production / (Concentration Ratio –1)
Example: 3450/(10-1) = 383.33 lbs./hr
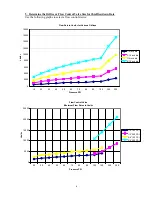
4. Determine if Continuous or Intermittent Sampling is Required
Use intermittent sampling when the boiler operation or loading is intermittent, or on boilers where the
required blowdown rate is less than 25% of the smallest available flow control valve or less than the flow
through the smallest orifice. See the graphs on the next page.
Use continuous sampling when the boiler is operating 24 hours per day and the required blowdown rate
is more than 25% of the smallest applicable flow control valve or orifice. See the graphs on the next
page.
Use of a flow control valve will give you the best control of the process, since the flow rate can be easily
adjusted. The dial on the valve also gives you a visual indication if the flow rate has been changed. If the
valve clogs, it can be opened to clear the obstruction, and closed to the previous position.
If an orifice plate is used, you must install a valve downstream from the orifice in order to fine tune the
flow rate and provide additional back pressure in many applications.
Example: An 80 psi boiler has a Required Blowdown Rate of 383.33 lbs./hr. The maximum flow rate of
the smallest flow control valve is 3250 lbs./hr. 3250 x 0.25 = 812.5 which is too high for continuous
sampling. Using an orifice, the flow rate through the smallest diameter plate is 1275 lbs./hr. This is too
high for continuous sampling.