42
6.
Thread cutting and automatic feed
6.1
Thread cutting
■
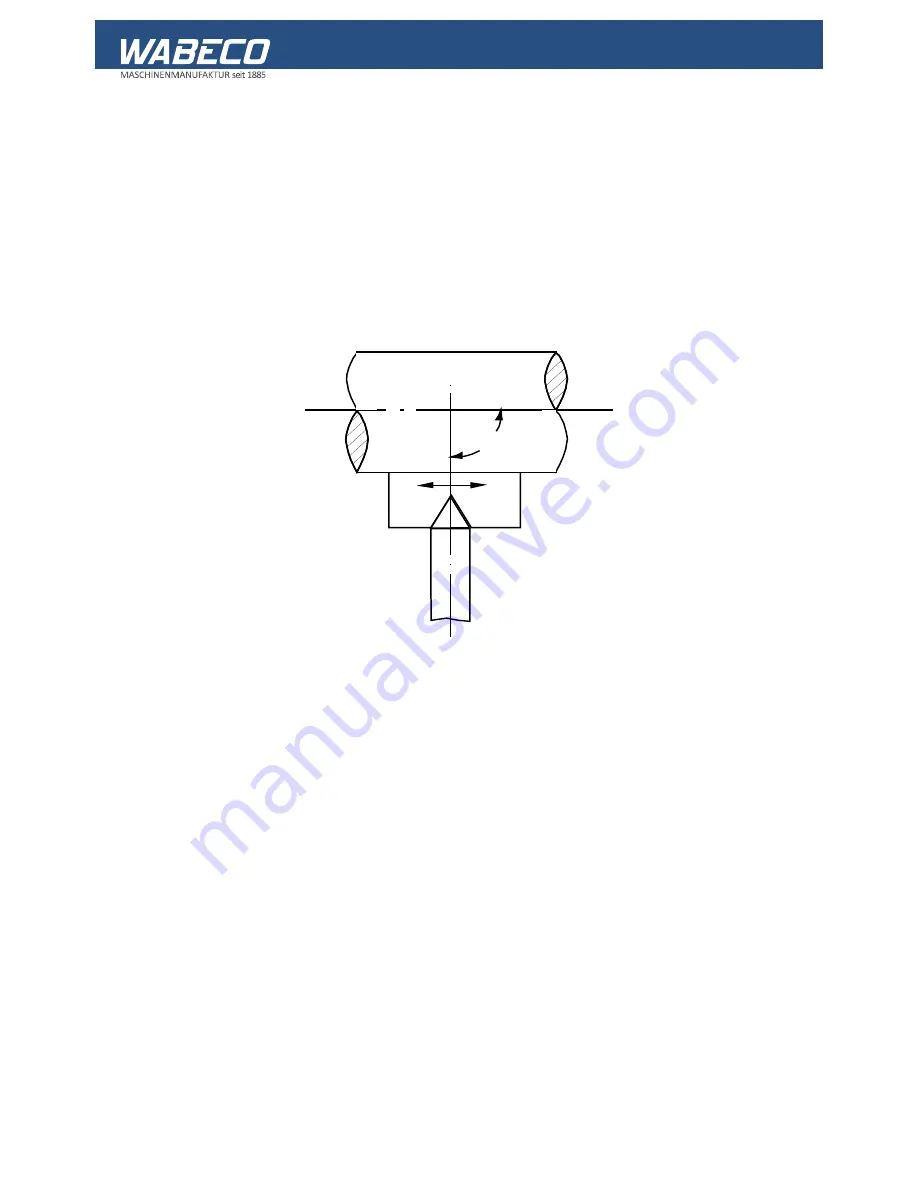
The thread turning steel is a moulded turning steel with the profile of the thread to be cut.
■
It is ground according to templates (Figure 1) and must be set precisely to the centre of the work
piece otherwise there will be a distortion in the thread profile.
■
In order to obtain the correct position of thread flanks to the work piece axis, place the grinding
gauge up against the work piece and use it to set the turning steel (Figure 1). To do this, push the
gauge up to both flanks of the turning steel, one after another.
Figure 1: Setting the thread turning steel
90°
■
The feed of the thread turning steel is carried out via the lead screw and must match the thread
gradient.
■
The change gears belonging to the accessories create the connection between the feed drives
and the lead screw.
■
By fitting different toothed wheel combinations, it is possible to cut metric and imperial right and left
threads.
■
The different axis intervals of the toothed wheels can be set by swivelling the quadrant and
adjusting the quadrant bolt.
Feed:
■
The feed is switched on using the switch lever on the lock plate.
■
The feed must always be switched on in order for the turning steel to return to the same position
when carrying out multiple cutting procedures.
■
After completing the cut, bring the turning steel with the transverse skid out of the inroad otherwise
the flanks and cutting edges will be damaged.
■
Then return the turning steel to the starting position by changing the direction of rotation of the
motor via the turn switch for forwards-reverse.
■
It is good if the thread end has a 4-5 mm wide clearance milled in order to better remove the
thread steel out of the way.
In the event of a long thread diameter, the turning centre point should always be used to prevent the
work piece from pushing away.
Summary of Contents for CC-D6000 hs
Page 76: ...76 18 Drawings and legends 18 3 Protective hood drive 2 0 kW motor...
Page 78: ...78 18 Drawings and legends 18 4 Electronic console 2 0 kW motor...
Page 86: ...86 18 Drawings and legends 18 10 Bed with lead screw with trapezoidal threaded spindle...
Page 90: ...90 18 Drawings and legends 18 11 Bed with lead screw with ball screw spindle...
Page 94: ...94 18 Drawings and legends 18 13 Tool skid Transverse skid...
Page 96: ...96 18 Drawings and legends 18 14 Tool skid Lock plate...
Page 98: ...98 18 Drawings and legends 18 15 Tool skid Longitudinal skid...
Page 100: ...100 18 Drawings and legends 18 16 Transverse skid with lock plate with ball screw spindle...
Page 102: ...102 18 Drawings and legends 18 17 Tailstock...
Page 104: ...104 18 Drawings and legends 18 18 Motor for control of the x axis...
Page 106: ...106 18 Drawings and legends 18 19 Motor for control of the z axis...
Page 108: ...108 18 Drawings and legends 18 20 Operating console for 1 4 kW motor...
Page 110: ...110 18 Drawings and legends 18 20 Operating console for 1 4 kW motor...
Page 112: ...112 18 Drawings and legends 18 21 Operating console for 2 0 kW motor...
Page 114: ...114 18 Drawings and legends 18 21 Operating console for 2 0 kW motor...
Page 116: ...116 18 Drawings and legends 18 22 Bracket arm for operating console...
Page 118: ...118 18 Drawings and legends 18 23 Industrial screen and membrane keyboard...
Page 138: ...138 19 Circuit diagram 19 9 Multiphase motor with end stop...
Page 154: ...154 23 Safety cabin optional 23 8 Drawing and legend...
Page 163: ...163 26 Tensioning bracket with milling machine table optional 26 7 Drawing and legend...






































