7
3. Battery Cabinet Installation
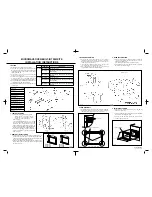
3.4 Internal Wiring (Typical)
• Battery cabinets use multiple 12 VDC batteries connected in series to provide nominal DC voltages ranging from 192 VDC to 480 VDC
(±240 VDC).
• Internal cabling is sized for specific application load currents. The insulated cables can be 2 AWG, 4 AWG, 1/0 AWG, 2/0 AWG, 4/0 AWG or
dual 2/0 AWG.
• Each battery cabinet includes a specific wiring diagram.
• All circuit breakers are in the top tier of the battery cabinet, except for model BP480V200, which contains the circuit breaker in the
bottom tier of the battery cabinet.
• All load connection polarities will be marked by a POS (+) or NEG (-) label (or an “N” center label for ±240 VDC strings).
• All battery cabinets are provided with a branch circuit overcurrent protection device and may be wired directly to the load or UPS.
• If the battery cabinet includes an integrated battery charger (single-phase and “C” models only), the internal cabinet wiring will be
preinstalled and the charger will include fusing for 120 VAC input. The integrated charger can also be powered at 208 VAC/20 A or 240
VAC/15 A with the appropriate fusing replaced.
The charger input must be connected to a separate AC supply circuit, not the UPS
system.
3.5 Preliminary Electrical Check
1. Reset the circuit breaker to the “on” position and measure the battery cabinet output voltage at the output load connection points.
(Measure voltage with a digital voltmeter.)
2. The measured voltage should approximately match the voltage listed on the battery cabinet nameplate. The battery cabinet output
voltage will be equal to the number of individual batteries installed in series multiplied by the unit voltage. (For example: 40 batteries x
12.84 VDC = 513.6 VDC output.)
3. If the measured voltage is significantly different than anticipated, determine the cause (e.g. low charge, shorted cell, reversed battery,
faulty wiring) and correct the voltage disparity before proceeding.
4. Set the circuit breaker to the “off” position as a safety precaution during installation.
3.6 Battery Cabinet Placement
Place the battery cabinet in a cool location with free airflow that is away from direct heat sources. The lifespan and performance of a battery
can be affected dramatically by elevated temperature, decreasing 50% for each 15° F above 77° F.
1. Prepare the surface where the cabinet will be placed. The surface must be clean, flat and able to support the battery cabinet and other
equipment installed nearby. (See
Section 7.1
for floor loading specifications.)
2. Allow adequate clearance around the front and rear of the battery cabinet for ventilation and maintenance. The front door must be
accessible to allow easy access to internal batteries, internal fuses and other overcurrent protection devices. (See
Section 7.1
for
dimensions. See
Section 6.1
for detailed battery cabinet measurements.)
3. If the cabinet will be anchored to the floor, install appropriate anchor bolts in the mounting hole at the bottom of the cabinet. Use
washers to create a level surface between the mounting areas around the anchor bolts.
4. Using extreme caution, remove the bolts securing the battery cabinet to the shipping pallet.
5. If the cabinet does not have casters proceed to step 8. For cabinets with casters, remove the mount brackets from the cabinet to allow
the cabinet to roll freely on the casters. This can be done by loosening the nuts between the leveling feet and the mount brackets.
6. Cabinets with casters are packaged on shipping pallets with a heavy duty ramp. Lower the ramp and with extreme caution, move the
cabinet down the ramp and into position.
7. If the cabinet with casters is to be secured to the floor, reinstall the mount brackets and mark the floor to install the appropriate floor
anchors and secure in place.
8. For cabinets without casters, forklift forks should be at maximum width within the cabinet clearance opening and fully inserted to prevent
tipping. Lift cabinet from bottom only. Be careful not to damage the sheet metal floor of the cabinet with the forks.
9. If the battery cabinet will be secured to the floor, carefully align and lower the battery cabinet down on the floor anchor bolts and secure
it in place.
10. If the cabinet will not be secured to the floor, lower it into the designated space and then level it using shims. (Leveling does not affect
performance but does align the battery cabinet with other equipment in the facility.)
Summary of Contents for BP192V787C-1PH
Page 12: ...12 Dimensions INCHES cm 6 Diagrams 6 1 2 All BP240V Models 3 Shelves...
Page 13: ...13 6 Diagrams 6 1 3 BP480V200 Model 4 Shelves Dimensions INCHES cm...
Page 14: ...14 Dimensions INCHES cm 6 Diagrams 6 1 4 BP480V300 and BP480V400 Models 4 Shelves...
Page 15: ...15 6 Diagrams 6 1 5 BP480V500 Model 4 Shelves Dimensions INCHES cm...
Page 38: ...38 Dimensiones PULGADAS cm 6 Diagramas 6 1 2 Todos los Modelos BP240V 3 Repisas...
Page 56: ...56 2 0 40 C 25 C C VW 1 FT 1 C...
Page 57: ...57 2 Tripp Lite 24 3 24 C Tripp Lite...
Page 58: ...58 3 2 3 1 8 3 2 1 Tripp Lite 2 3 3 3 1 2 3 4 C Tripp Lite 5 7 2 6 7 8...
Page 62: ...62 5 5 1 1 25 C 25 C 8 25 50 33 2 13 2 14 2 3 1 2 3 100 10 4 4 1 2 7 2 3...
Page 63: ...63 6 6 1 6 1 1 BP192V787C 1PH 2 c...
Page 64: ...64 6 6 1 2 BP240V 3 c...
Page 65: ...65 6 6 1 3 BP480V200 4 c...
Page 66: ...66 6 6 1 4 BP480V300 BP480V400 4 c...
Page 67: ...67 6 6 1 5 BP480V500 4 c...
Page 68: ...68 6 6 2 6 2 1 192 UL MTW 105 C UL 600 UL 50 600 42 216 221 120 208 240 192 218 218...
Page 69: ...69 6 6 2 2 240 UL MTW 105 C UL 600 UL 70 600 42 270 276 240 273 120 208 240 273...
Page 70: ...70 6 6 2 3 240 UL MTW 105 C UL 600 UL 150 600 42 1 2 3...
Page 71: ...71 6 6 2 4 240 UL MTW 105 C UL 600 UL 250 600 42 N...
Page 72: ...72 6 6 2 5 EBP 120 UL MTW 105 C CSB HRL FR UL 600 6 250 MCM 1 11 20 120 120 240...
Page 75: ...75 6 6 3 7 A c 120 208 240 60 13 65 0 15 30 120 20 208 20 240 15 A Charger OK...
Page 79: ...79...
Page 80: ...80 1111 W 35th Street Chicago IL 60609 USA www tripplite com support 19 02 084 93 3390_RevE...