FUNCTION CHARACTERISTICS
96
NA20 - Manual - 04 - 2022
With traditional selective logic systems, in the absence of suitable cares, the event of a circuit
breaker failure causes the block of the receiving relays situated upstream the circuit breaker, so the
fault cannot be cleared.
When using the Pro-N devices inside the selective logic systems, the answer to the circuit breaker
failure problem can be solved by means of, (as well as the BF-Breaker Failure element) or by means
of a threshold adjusted for time selectivity, through use of the output block reset timer too with the
intent that avoid permanently block of all upstream relays by downstream block signals (the only one
unblocked relays deals to the fault breaker).
The
t
F-IPh
,
t
F-IE,
t
F-IPh/IE
timers must be adjusted according the following rule (example for
t
F-Iph
):
t
F-Iph
= t + T
AP
+ t
rip
+
e
t
+
e
s
where t is the larger phase protection operate time, T
AP
is the circuit breaker operate time (with arc
extinction), t
rip
is the larger reset time of all protective relays inside the selective logic system,
e
t
is
an potential selectivity margin relative to the
t
F-x
time of the downstream relays,
e
s
is a safety margin
need to include timers errors (tolerances).
Diagnostic
To guarantee maximum fail-safety, the relay performs a run time monitoring for pilot wire continuity
and pilot wire shorting.
[1]
Exactly the output blocking circuit periodically produces a pulse, having a small enough width in
order to be ignored as an effective blocking signal by the input blocking circuit of the upstream
protection, but suitable to prove the continuity of the pilot wire.
Furthermore a permanent activation (or better, with a duration longer than a preset time) of the
blocking signal is identified, as a warning for a possible short circuit in the pilot wire or in the output
circuit of the downstream protection.
The periodic pulses that are sent by output circuit may be enabled or disabled by means the
Pulse
-
BLOUT1
parameter available inside the
Set \ Pilot wire diagnostic
menu; with OFF setting the
pulses are disabled.
[2]
If no pulses are received inside an adjustable time window at the selective block input circuit, a
break pilot wire alarm is issued; the information is available for reading (
Breaked BLIN1
data inside
Read \ Pilot wire diagnostic
submenu) and can drive an output relay and or a LED (
PulseBLIN-K
and or a
PulseBLIN-L
parameters inside
Set \ Pilot wire diagnostic
submenu).
Note 1 Full diagnostic of pilot wires is only available when committed pilot wire input/outputs are employed
Note 2 When several outputs are parallel linked the pulse emission must be enabled inside one device only, sooner inside the outermost device
Pilot wire output
Pilot wire link
≥
1
Pulse
generator
BLOCK OUT
BLOCK IN
T
0
Pilot wire
Diagnostic
Pilot wire input
No pulses
Permanently “ON”
BLIN1
BLOUT1
Breaked BLIN
TR
IP
PIN
G
M
AT
RIX
(
LE
D+R
EL
AY
S)
Shorted BLIN
Pulse BLIN1
Pulse BLIN1
Pulse BLOUT1
Pulse BLOUT1
Block2-diagram.ai
Pilot wire output
BLOUT1
TR
IP
PIN
G
M
AT
RIX
(
LE
D+R
EL
AY
S)
ModeBLOUT1
A
B
C
D
≥
1
ST-Iph BLK2
ST-IE BLK2
&
Block2 output
(ON
≡
Enable)
I>BLK2OUT
Start
I>
BLK2OUT-Iph
BLK2OUT-Iph/IE
BLK2OUT-IE
A = OFF
B = ON IPh
C = ON IPh/IE
D = ON IE
BLK2OUT-IPh-K
BLK2OUT-IPh-L
BLK2OUT-IPh/IE-K
BLK2OUT-IPh/IE-L
BLK2OUT-IE-K
BLK2OUT-IE-L
≥
1
Start
I
E
>>>
&
Block2 output
(ON
≡
Enable)
IE>>>BLK2OUT
I
E
>> Block2 OUT
I
E
> Block2 OUT
I
E
>>> Block2 OUT
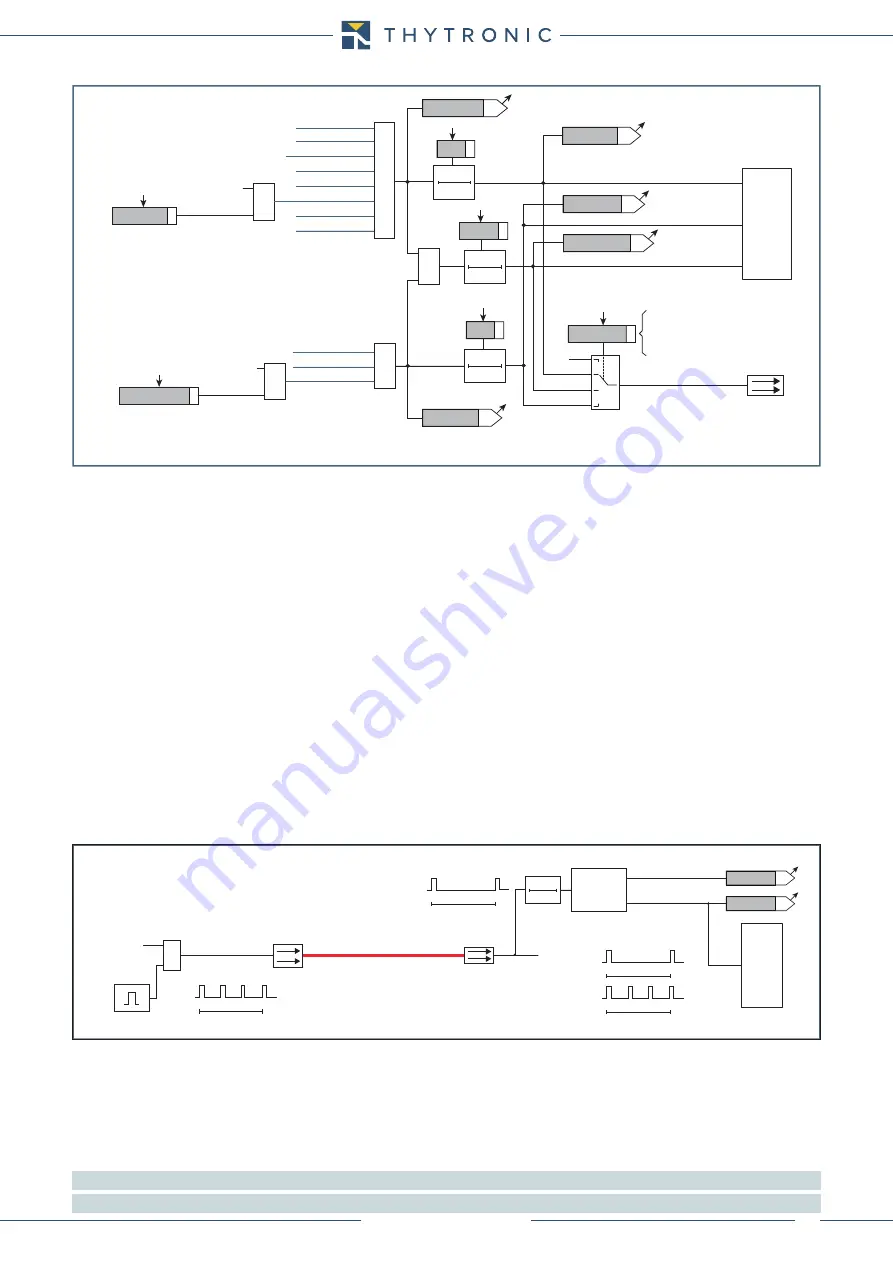
Logic diagram concerning the selective block output - Block2 output
≥
1
I
> Block2 OUT
I
>> Block2 OUT
I
2> Block2 OUT
I
2>> Block2 OUT
I
>>> Block2 OUT
DthAL1
Block2 OUT
DthAL2
Block2 OUT
Dth
Block2 OUT
t
F-IPh
t
F-IPh/IE
t
F-IE
T
0
t
F-IPh/IE
T
0
t
F-IPh
T
0
t
F-IE
Summary of Contents for NA20
Page 207: ...APPENDIX 207 NA20 Manual 04 2022...






























