Chapter |
Appendix 2: Optical paths of X-Rays in ARL EQUINOX 5000/5500
Confidential, limited rights
PN AA83865 | Revision A | 25-Oct-2019
Instruction Notice, ARL EQUINOX 5000-5500
Page
51
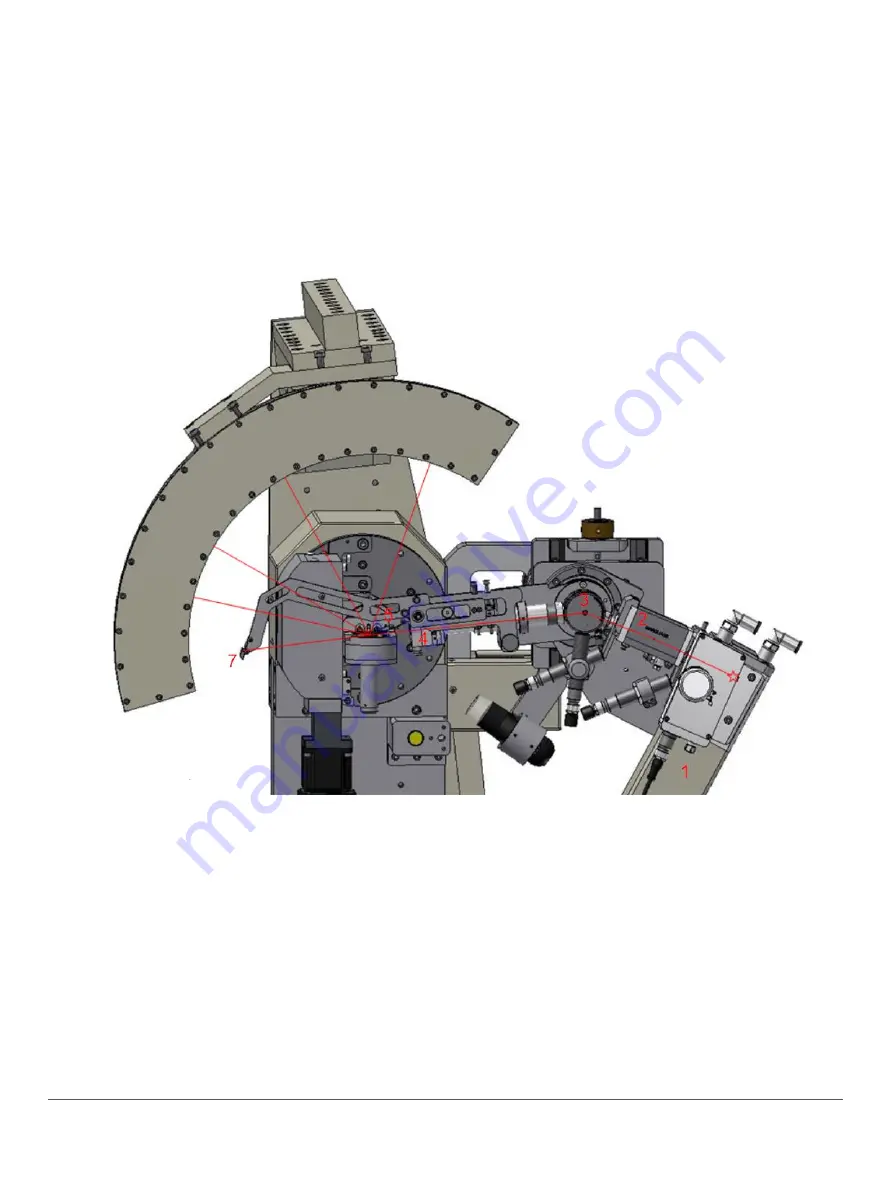
6.
The beam stop blocks the direct beam. A proper adjustment of this plate allows to improve
the low angle detection.
11.3 Mirror and Monochromator Configuration
The figure shows an ARL EQUINOX 5000 with a CPS120 detector. For the ARL EQUINOX
5500 that is equipped with a CPS590 (bigger radius), the X -ray path is identical except that
the X-rays travel more distance up to the detector.
The figure above describes the X-Ray beam propagation inside of the enclosure when the
shutter is opened and with a mirror-monochromator configuration. During this operation, the
enclosure is closed and door is locked.
1.
X-Ray source emission. Scattering is emitted in all directions. The tubeshield is limiting the
X-Rays.
2.
X-Ray mirror allows capturing a given solid angle from the direct beam and emits a
parallel and monochromatic beam to the monochromator.
3.
The monochromator crystal allows capturing the parallel beam from the mirror and emits a
narrow parallel and monochromatic beam.
4.
Primary crossed slits can shape the incident beam (from 0.2 to 0.5 mm for analysis of
samples).






















