SLOU186F
–
AUGUST 2006
–
REVISED AUGUST 2010
The MSB (bit 7) determines if the word is to be used as a command or as an address. The last two
columns of
show the function of the separate bits if either address or command is written. Data
is expected once the address word is sent. In continuous-address mode (Cont. mode = 1), the first data
that follows the address is written (or read) to (from) the given address. For each additional data, the
address is incremented by one. Continuous mode can be used to write to a block of control registers in a
single stream without changing the address; for example, setup of the predefined standard control
registers from the MCU
’
s non-volatile memory to the reader. In non-continuous address mode (simple
addressed mode), only one data word is expected after the address.
Address mode is used to write or read the configuration registers or the FIFO. When writing more than 12
bytes to the FIFO, the continuous address mode should be set to 1.
The command mode is used to enter a command resulting in reader action (initialize transmission, enable
reader, and turn reader On/Off...)
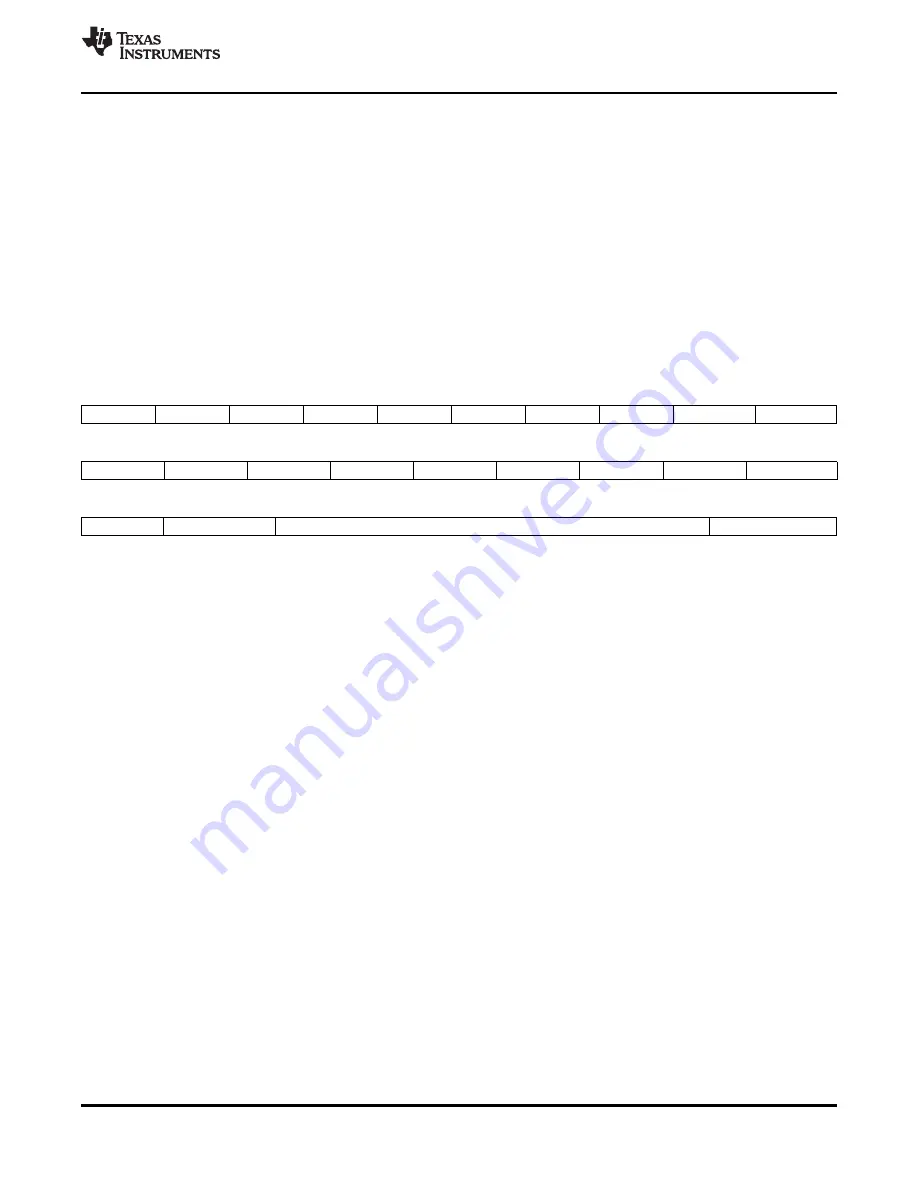
An example of expected communication between MCU and reader is shown below.
Continuous address mode
Start
Adr x
Data(x)
Data(x+1)
Data(x+2)
Data(x+3)
Data(x+4)
...
Data(x+n)
StopCont
Non-continuous address mode (single address mode)
Start
Adr x
Data(x)
Adr y
Data(y)
...
Adr z
Data(z)
StopSgl
Command mode
Start
Cmd x
(Optional data or command)
Stop
Copyright
©
2006
–
2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
System Description
37
focus.ti.com:
















































