Start
Condition
CLK
I/O_[7]
I/O_[6:0]
a0 [6:0] d0 [6:0]
xx
d1 [6:0] d2 [6:0]
dN [6:0]
d3 [6:0]
xx
StopCont
Valid Ouput Data
a0 [7]
d0 [7]
d2 [7]
dN [7]
d1 [7]
d3 [7]
Internal OE
Output Data
50 ns
SLOU186F
–
AUGUST 2006
–
REVISED AUGUST 2010
5.6.1
Receive
At the start of a receive operation (when SOF is successfully detected), B6 is set in the IRQ status
register. An interrupt request is sent to the MCU at the end of the receive operation if the receive data
string was shorter than or equal to 8 bytes. The MCU receives the interrupt request, then checks to
determine the reason for the interrupt by reading the IRQ status register (address 0Ch), after which the
MCU reads the data from the FIFO.
If the received packet is longer than 8 bytes, the interrupt is sent before the end of the receive operation
when the ninth byte is loaded into the FIFO (75% full). The MCU should again read the content of the IRQ
status register to determine the cause of the interrupt request. If the FIFO is 75% full (as marked with flag
B5 in IRQ status register and by reading the FIFO status register), the MCU should respond by reading
the data from FIFO to make room for new incoming receive data. When the receive operation is finished,
the interrupt is sent and the MCU must check how many words are still present in the FIFO before it
finishes reading.
If the reader detects a receive error, the corresponding error flag is set (framing error, CRC error) in the
IRQ status register, which indicates that the MCU reception was completed incorrectly.
5.6.2
Transmit
Before beginning data transmission, the FIFO should be cleared with a reset command (0F). Data
transmission is initiated with a selected command (described in the
section,
). The MCU then commands the reader to do a continuous write command (3Dh, see
) starting from register 1Dh. Data written into register 1Dh is the TX length byte1 (upper and
middle nibbles), while the following byte in register 1Eh is the TX length byte 2 (lower nibble and broken
byte length). Note that the TX byte length determines when the reader sends the EOF byte. After the TX
length bytes are written, FIFO data is loaded in register 1Fh with byte storage locations 0 to 11. Data
transmission begins automatically after the first byte is written into the FIFO. The loading of TX length
bytes and the FIFO can be done with a continuous-write command, as the addresses are sequential.
At the start of transmission, the flag B7 (Irq_tx) is set in the IRQ status register. If the transmit data is
shorter than or equal to 4 bytes, the interrupt is sent only at the end of the transmit operation. If the
number of bytes to be transmitted is higher or equal to 5, then the interrupt is generated. This occurs also
when the number of bytes in the FIFO reaches 3. The MCU should check the IRQ status register and
FIFO status register and then load additional data to the FIFO, if needed. At the end of the transmit
operation, an interrupt is sent to inform the MCU that the task is complete.
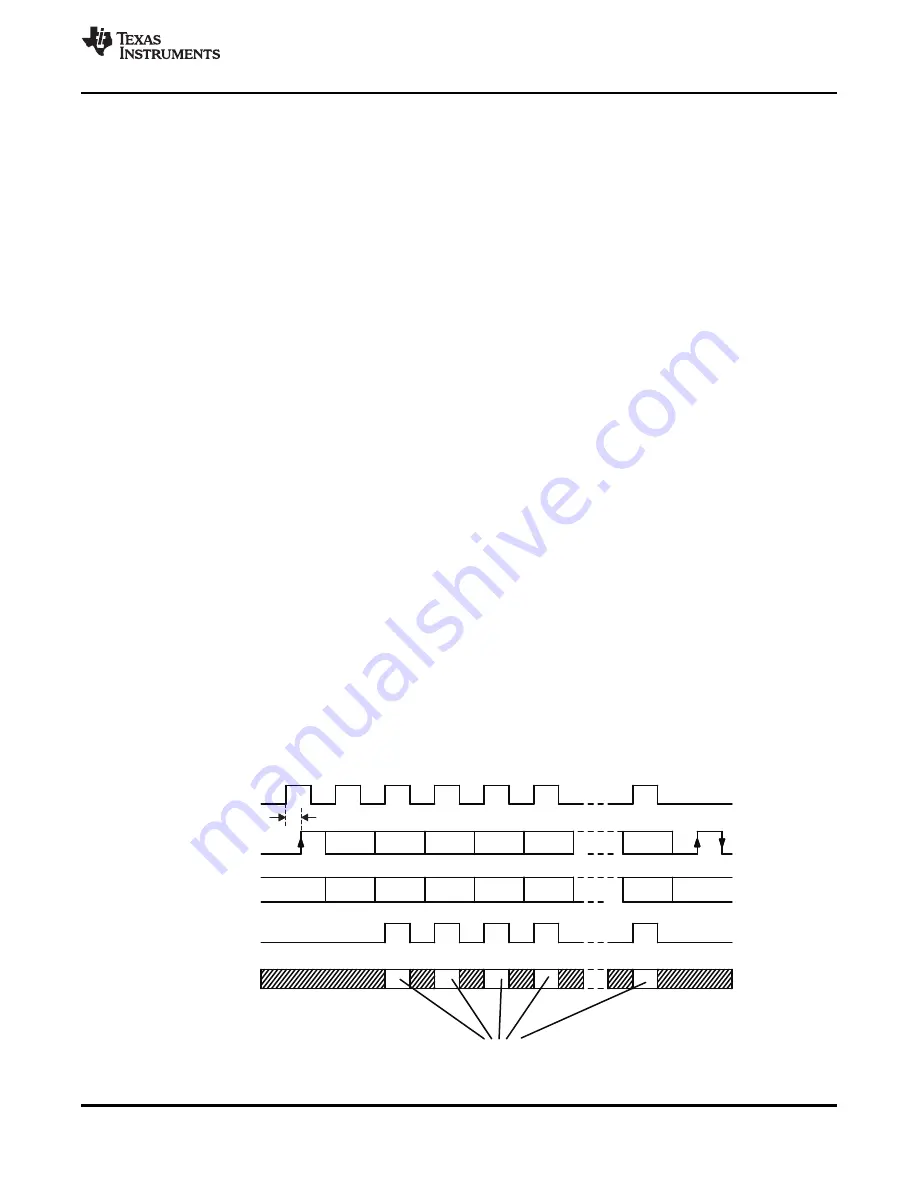
Figure 5-7. Data Output Only When CLK Is High
Copyright
©
2006
–
2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
System Description
39
focus.ti.com:















































