MEM_alloc
Application Program Interface
2-215
When using the large memory model, the MEM module divides heaps
that cross page boundaries into memory blocks that do not cross
boundaries. As a result, MEM_alloc and MEM_free can only allocate and
free memory within a single memory block, and the largest block that
MEM_alloc can allocate in any case is 64K words (0x10000).
For example, suppose you create a RAM segment called MYRAM that is
100K words in length. MYRAM has a base address of 2:F000 and a
length of 0x19000. The heap within MYRAM is also 100K words and has
a heap identifier label of MYSEG. So this heap also has a base address
of 2:F000 and ends at 4:7FFF.
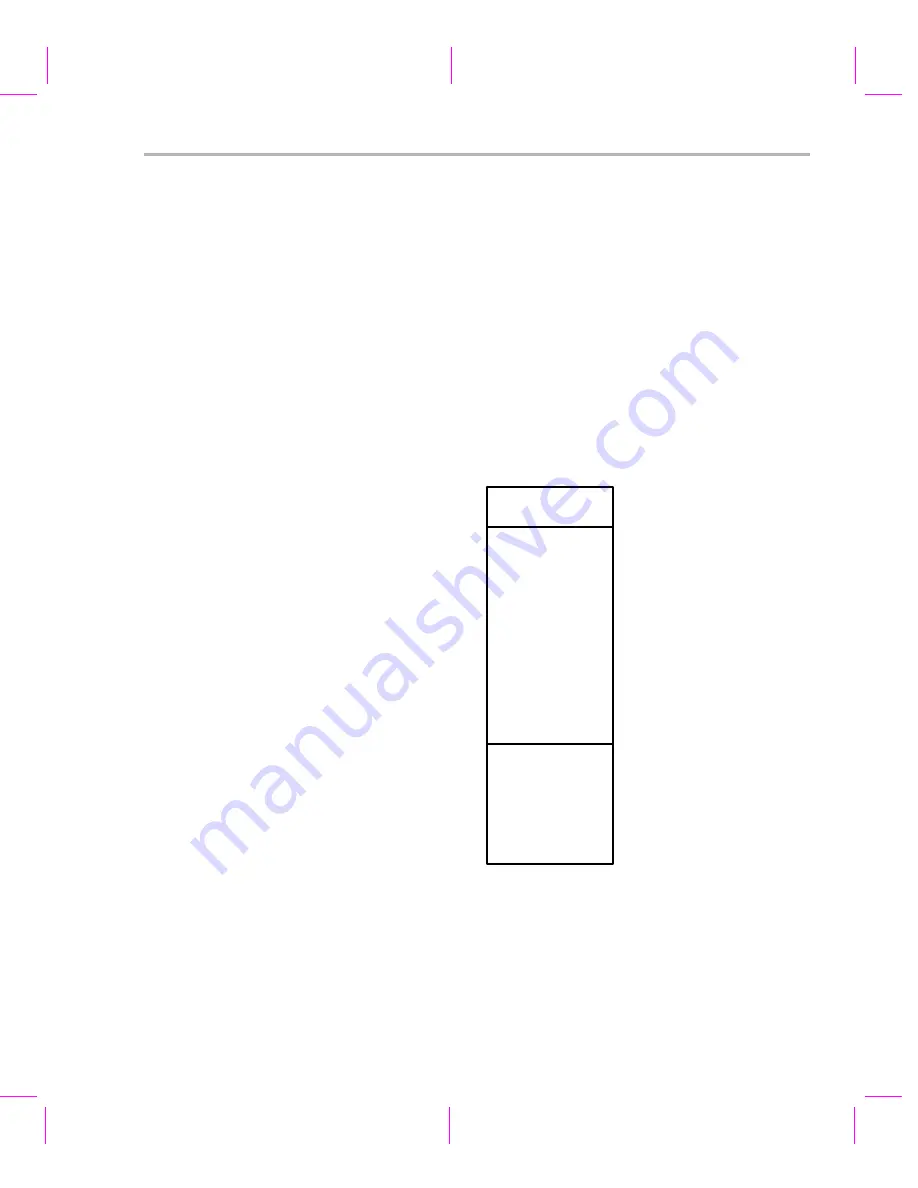
To prevent a memory block from crossing a page boundary, the MEM
Module separates this heap into the following memory blocks, which are
aligned along 64K page boundaries:
Figure 2-1.
MYSEG Heap Initial Memory Map
Suppose your program calls MEM_alloc in the following sequence:
P3 = MEM_alloc(MYSEG, 0xFF80, 0);
P1 = MEM_alloc(MYSEG, 0x6000, 0);
P2 = MEM_alloc(MYSEG, 0x1800, 0);
P4 = MEM_alloc(MYSEG, 0x800, 0);
2:F000
3:0000
3:FFFF
4:0000
4:7FFF
2:FFFF
Block 1
Length 0x1000 (4K words)
Block 2
Length 0x10000 (64K words)
Block 3
Length 0x8000 (32K words)






























