A single Ranger Gateway can be joined with up to 250 ZoneRangers. Given that each Ranger Gateway
instance typically serves a single management application instance, this allows a given management
application to extend its reach into many firewall-partitioned networks, providing that one or more
ZoneRangers have been installed in each such network. Similarly, each ZoneRanger can be joined with
up to 250 Ranger Gateway instances, allowing managed devices in the firewall-partitioned network
where the ZoneRanger has been installed to interact by proxy with a large number of management
applications. The many-to-many joining relationship between Ranger Gateways and ZoneRangers is
illustrated in the following figure.
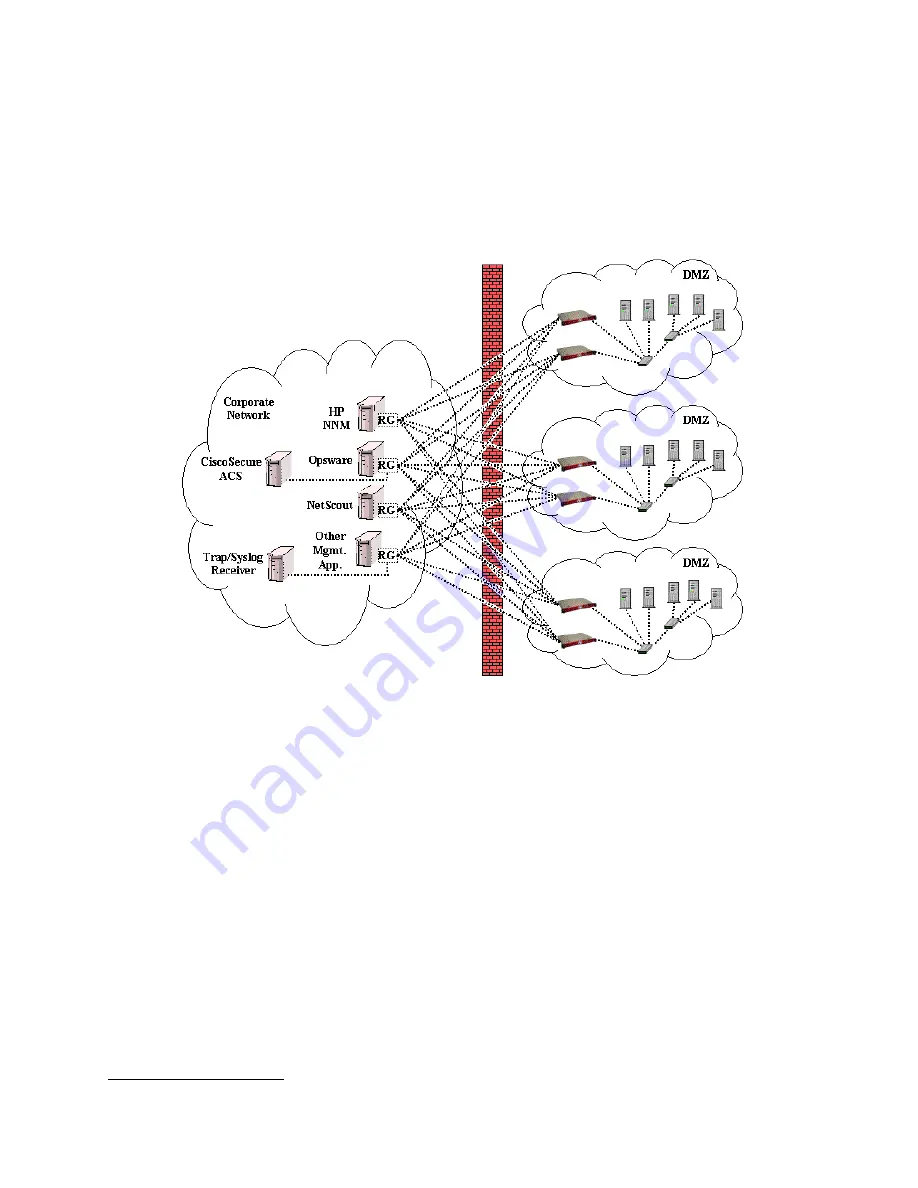
Figure 9-1. Many to Many ZoneRanger configuration
The figure shows four Ranger Gateway instances, each joined with six ZoneRangers. Each of the
ZoneRangers is joined with all four Ranger Gateways. The number of joining relationships that need to
be established, then, depends on the number of management applications being used, and the number of
firewall-partitioned networks to be managed.
If there is a firewall between a Ranger Gateway and a ZoneRanger that need to be joined, as is typically
the case, a firewall rule must be configured, to allow the Ranger Gateway and ZoneRanger to
communicate. All management protocol traffic being proxied between a Ranger Gateway and a
ZoneRanger is multiplexed over a single TCP connection, so a single TCP firewall rule, specifying the
configured messaging port
5
as the destination port is all that is required.
Note that the figure also shows two management applications: CiscoSecure ACS and a Trap/Syslog
Receiver that make use of a Ranger Gateway installed on a different server. This approach can be used
to reduce the number of Ranger Gateway instances, and associated firewall rules and joining
relationships, in cases where the nature and volume of the protocol traffic allows.
5
The default messaging port is TCP 4854.
ZoneRanger 5.5 User's Guide
33






























