HRL
Series
Cooling Capacity Calculation
HRL200-A
Required Cooling Capacity Calculation
Example 3: When there is no heat generation, and when cooling the object below a certain temperature and period of time.
Heat quantity by cooled substance (per unit time) Q : Unknown [W] ([J/s])
Cooled substance
: Water
Cooled substance mass m
: (=
ρ
x V) [kg]
Cooled substance density
ρ
: 1 [kg/L]
Cooled substance total volume V
: 250 [L]
Cooled substance specific heat
C
: 4.186 x 10
3
[J/(kg·K)]
Cooled substance temper
ature when cooling begins
T
0
: 305 [K] (32 [
°
C])
Cooled substance temper
ature after t hour
T
t
: 293 [K] (20 [
°
C])
Cooling temperature difference T
: 12 [K] (= T
0 –
T
t
)
Cooling time t
: 900 [s] (= 15 [min])
∗
Refer t
o th
e following for t
h
e typical p
h
ysical property values by circulatin
g flui
d.
Q = =
= = 13953 [J/s]
≈
14.0 [kW]
Cooling capacity = Considering a safety factor of 20%,
14.0 [kW] x 1.2 =
m x C x (T
0
– T
t
)
t
ρ
x V x C x T
t
1 x 250 x 4.186 x 10
3
x 12
900
16.8 [kW]
Precautions on Cooling Capacity Calculation
1. Heating capacity
When
the
circulating
fluid
temperature is set above room temperature, it needs to be
heated
by
the
the
r
mo-chille
r.
The
heating
capacity depends on
the
circulating
fluid tempe
rature.
Consider the
radiation r
ate and heat capacity of the user’s equipment and che
ck bef
orehand if the required heating capacity is pr
ovided.
2. Pump capacity
<Cir
culating fluid fl
ow rate>
Circulating
flui
d
fl
ow rate varies depending on t
h
e circulating
fl
uid dis
ch
arge pressure. Consider t
he
installation
h
ei
gh
t difference
between
the
the
r
mo-chiller
and
the
user
’
s equipment, and
the
piping resistance
such
as circulating
fluid
pipings, or piping size, or
piping curv
es in the machin
e.
Che
ck bef
orehand if the required fl
o
w is achi
ev
ed, using the pump capacity cu
rves.
<Cir
culating fluid dis
charge pressure>
Circulating fluid discharge pressure has the possibility to increase up to the maxi
m
um pressure in the pump capacity cu
rves.
Che
ck bef
orehand if the circulating fluid pipings or circulating fluid circuit of the user’
s equipment are fully durab
le against this pressur
e.
Circulating Fluid Typical Physical Property Values
1. This catalog uses the following values f
or density and specific heat in calculating the required cooling capacit
y.
Density
ρ
: 1 [kg/L] (or, using conventional units, w
eight
volume ratio = 1 [kgf/L] )
Specific heat
C: 4.19 x 10
3
[J/(kg·K)] (or, using conventional units, 1 x 10
3
[cal/(kgf·
°
C)])
2. Values f
or density and specific heat
change slightly according to temperature shown below. Use this as a reference.
Water
P
h
ysical property
value
Temperature
Density
ρ
[kg/L]
Specific heat C
[J/(kg·K)]
Conventional units
Weight volume ratio [kgf/L] Speci
fi
c heat C [cal/(kgf·
°
C)]
5
°
C
1.00
4.2 x 10
3
1.00
1 x 10
3
10
°
C
1.00
4.19 x 10
3
1.00
1 x 10
3
15
°
C
1.00
4.19 x 10
3
1.00
1 x 10
3
20
°
C
1.00
4.18 x 10
3
1.00
1 x 10
3
25
°
C
1.00
4.18 x 10
3
1.00
1 x 10
3
30
°
C
1.00
4.18 x 10
3
1.00
1 x 10
3
35
°
C
0.99
4.18 x 10
3
0.99
1 x 10
3
40
°
C
0.99
4.18 x 10
3
0.99
1 x 10
3
Example of conventional units (Reference)
Heat quantity by cooled substance (per unit time) Q : Unkno
wn [cal/h]
→
[W]
Cooled substance
: Water
Cooled substance w
eight
m
: (=
ρ
x V) [kgf]
Cooled substance w
eight
volume ratio : 1 [kgf/L]
Cooled substance total volume V
: 250 [L]
Cooled substance specific heat
C
: 1.0 x 10
3
[cal/(kgf·
°
C)]
Cooled substance temper
ature when cooling begins
T
0
: 32 [
°
C]
Cooled substance temper
ature after t hour
T
t
: 20 [
°
C]
Cooling temperature difference T
: 12 [
°
C] (= T
0
– T
t
)
Cooling time t
: 15 [min]
Conversion factor:
hours to mi
nutes
:
60 [min/h]
Conversion factor:
kcal/h to kW
:
860 [(cal/h)/W]
Q = =
=
≈
13953 [W] = 14.0 [kW]
Cooling capacity = Considering a safety factor of 20%,
14.0 [kW] x 1.2 =
m x C x (T
0
– T
t
)
t x 860
x V x 60 x C x T
t x 860
1 x 250 x 60 x 1.0 x 10
3
x 12
15 x 860
16.8 [kW]
∗
This is the calculated
value b
y changing the fluid tempe
rature only.
Thu
s, it var
ies substantially depending on the
w
ater bath or piping shap
e.
21
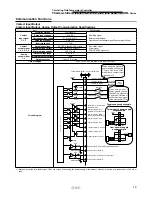
The
r
mo-chiller
Water bath
V
After 15 minutes, cool 32
°
C down to 20
°
C.
20
°
C
Q x t: Heat capacity [kJ]
21