7
Fig.e-4
Fig.e-5
Fig.e-6
exactly twice the distance between the center of the
reticule and the center of rotation. The center of rotation
lies midway between the center of the reticule and the new
position of Polaris. Do not turn any of the setscrews more
than one-quarter turn at a time or the reticule will
disengage from the setscrews. Do not over-tighten these
screws too much or the stress could fracture the reticule.
Now re-center Polaris under the cross in the middle of the
reticule using the Azimuth and Altitude adjustments.
Repeat the entire procedure until Polaris remains in the
center of the reticule when the mount is rotated about the
R.A. axis. With some practice, you should be able to align
the reticule with the R.A. axis to within about 2 arc-
minutes. You should never have to make this adjustment
again, unless the polar scope has been dropped,
disassembled, or if the polar scope is to be used on
another mount.
If Polaris is not visible from your area, a distant object
such as the top of a telephone pole or a mountaintop can
be used. These objects are larger than the image of a star,
so they will not provide as accurate an alignment, but they
will not move during this alignment procedure.
Using the Polarscope
Northern Hemisphere
There is only one easily visible star near the North
Celestial Pole. This star is Polaris. The rest of the stars in
Ursa Minor are around Magnitude 5 and require very dark
skies to become visible. Since Polaris is not exactly on the
North Celestial Pole, the telescope's R.A. axis must be
offset from Polaris by a small amount in the correct
direction.
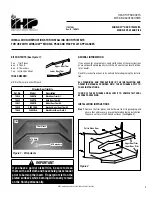
By using the line drawings of the Big Dipper and
Cassiopeia, the RA shaft can be rotated so the view in the
pole finder is similar to the view of the sky. This can be
done by using one eye to look through the pole finder
while using the other eye to look at the sky. This procedure
takes some practice. Adjust the mount in Altitude and
Azimuth, until Polaris is in the small circle on the line in the
pole finder (Fig.e-5). The polar alignment is now complete.
This should get the mount's R.A. axis within 5 arc-minutes
of the celestial pole.
Southern Hemisphere
There is a 4-star pattern in the polar scope, which
resembles the bucket of the Big Dipper. In the Southern
Hemisphere, there is an Asterism in Octans, which has
this shape. By rotating the R.A. axis and by adjusting
the altitude and azimuth of the mount, the four stars in
the Asterism can be placed in the circles in the Pole
Finder (Fig.e-6). This procedure can be somewhat
difficult in the city because all four of these stars are
fainter than Magnitude 5.
Place Polaris here
(half the distance)
If Polaris drifted to here
Polaris
NCP
Octans
C
a
ss
io
p
e
ia
B
ig
D
ip
pe
r
Place Polaris
here
Northern Hemisphere
Place the four stars
in the Asterism here
Polaris
NCP
Octans
C
a
s
s
io
p
e
ia
B
ig
D
ip
p
er
Southern Hemisphere
Summary of Contents for EQ6
Page 24: ...VI...