Parameterizing
3.2 MOBY commands
FC 45
3-20
Function manual, Release 03/2006 , J31069-D0167-U001-A2-7618
Programming
There are two programming methods.
•
Reading (processing) each MDS which comes by. After the ASM is programmed with a
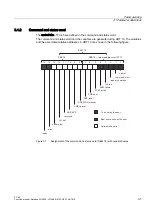
command, repeat_command is set and remains set. The following diagram shows the
primary states.
7KHXVHUVWDUWVKLVKHUFRPPDQG
IDVWHUWKDQWKH0'6VFDQSDVVWKH
ZULWHUHDGGHYLFH
7KHUHVXOWLVDYDLODEOHWRWKHXVHU
UHDG\ LPPHGLDWHO\DIWHUWKH
FRPPDQGLVSURFHVVHG$60BEXV\
7KH0'6VSDVVE\WKHZULWHUHDG
GHYLFHIDVWHUWKDQWKHXVHUFDQIHWFK
WKHUHVXOWV,QVXFKFDVHVWKHUHVXOWV
DUHLQWHUPHGLDWHO\VWRUHGRQWKH$60
7KHUHVXOWVDUHWKHQUHDGODWHU
5HVXOWVDUH
IHWFKHGRQWKH
$60
UHDG\
FRPPDQGBVWDUW
UHSHDWBFRPPDQG
$60BEXV\
$1=B0'6BSUHVHQW
Figure 3-2
Continuous reading of each passing MDS/transponder (repeat_command remains set)
When permanent command repetition is used, data may be transferred to the FC 45 slower
than new MDSs are being processed (fast MDS sequence, slow data transmission). In such
cases, the results are intermediately stored on the ASM. The ASM has a number of buffers
for this intermediate storage. When the buffers are full and the FC 45 has not fetched data
and additional MDSs arrive, these MDSs are no longer processed.
Table 3-17 Number of buffers on the ASM
ASM type
No. of buffers per channel
Max. user data which can be
processed with command
repetition
ASM 475/473
ASM 454
ASM 754
ASM 854
ASM 452
Write/read device U92*
Write/read device D10
RF300
70
39
9
39
3
150
100
246
16310 bytes
9087 bytes
2097 bytes
9087 bytes
699 bytes
34950 bytes
23300 bytes
57318 bytes
*) The number of buffers described here can always be used by MOBY U regardless of the ASM
type.
One buffer can hold up to 233 bytes of user data.