Mechanical properties of the motors
3.6 Radial and axial forces
1FT7 Synchronous Motors
Configuration Manual, (PFT7S) 01/2009, 6SN1197-0AD13-0BP2
67
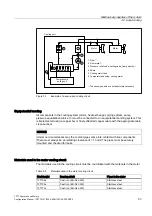
Radial force, 1FT7 Compact, AH 100
[>PP@
)
5'(
>1@
Q USP
Q USP
Q USP
Q USP
Q USP
Figure 3-9
Radial force F
R
at a distance x from the shaft shoulder for a statistical bearing lifetime of
25,000 h
3.6.4
Axial force stressing
When using, for example, helical toothed wheels as the drive element, in addition to the
radial force, there is also an axial force on the motor bearings. For axial forces, the spring-
loading of the bearings can be overcome so that the rotor is displaced corresponding to the
axial bearing play present.
Shaft height
Displacement
36 and 48
Approx. 0.2 mm
63 to 100
Approx. 0.35 mm
An axial force as large as the spring-loading is not permitted (100 ... 500 N). Premature
failure is the result when the bearing is not pre-tensioned.
Calculating the permissible axial force: F
A
= F
R
• 0.35
WARNING
Motors with integrated holding brake cannot be subject to axial forces!
Summary of Contents for 1FT7 Series
Page 2: ......
Page 12: ...Preface 1FT7 Synchronous Motors 12 Configuration Manual PFT7S 01 2009 6SN1197 0AD13 0BP2 ...
Page 251: ......