external timers, such as photoelectric sensors or incremental encoders, enable reading
pulses independent of the control. The reading results are provided for further process‐
ing by the data interfaces.
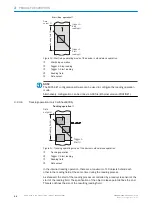
In principle, the codes can be recorded on any side on still or moving objects in a con‐
veyor system (single-side reading).
By combining several devices, it is possible to record several sides in one passage
(multi-side reading).
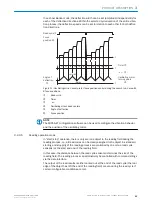
To record the codes, the device generates a scan line (line scanner).
When designed as a raster scanner, the device generates eight scan lines which are
offset parallel to each other.
Line scanner with oscillating mirror
The oscillating mirror also moves the scan line vertically to the scan direction from the
resting position to both sides with a low oscillation frequency. This means that the
device can also scan larger areas for bar codes.
NOTE
When starting up the device, the oscillating mirror may cause increased volume devel‐
opment.
The length of the scan line which can be used for evaluation (reading field height)
depends on the reading distance as a result of the V-shaped light emission.
The light pattern reflected from the bar code is recorded, processed, and decoded.
External sensors deliver information about the read cycle and conveyor speed (incre‐
ment) to control this process. The read results are output to the device data interfaces
and forwarded to a host/PC.
Detailed wiring of the device and the connections to the host/PC and the external sen‐
sors are described in chapter
.
NOTE
The CDB620 connection module with additional circuit board (
tion modules to devices with heating", page 48
) or the CDM420 connection module
with additional terminal (
see "Connecting the supply voltage", page 51
) is to be used
for devices with heating.
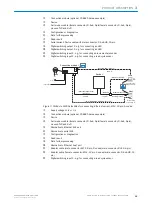
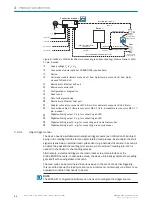
Block diagrams
Input 2
à
Input 1
á
Output 1
ß
Output 2
9
Device
3
"Serial RS-232/RS-422/485" (Host)
Connection module
2
Serial
Serial
Configuration
Diagnostics
5
SOPAS
SOPAS
"Power/SerialData/CAN/I/O"
(Aux, Host)
...
...
1 2
V
S
GND
Host
PC
“Serial RS-232” (Aux 1)
V
S
1
Further data
processing
6
Reading result
7
Cable
4
Cable
8
Figure 6: CLV63x to CLV65x facilities for connecting, serial variant
1
Supply voltage V
S
(V
S
= U
V
)
3
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
18
O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | CLV63x, CLV64x, CLV65x
8019588/129Z/2019-02-07 | SICK
Subject to change without notice