Chapter 5 Operations
Shield M10U user manual
31
5.1.1 Split-Bypass Input
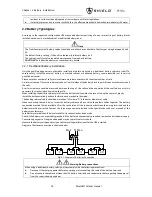
Fig. 5-1 illustrates the Modular UPS in what is known as the split-bypass configuration (that is, the bypass uses a separated
AC power). In this configuration, the static bypass and maintenance bypass share the same independent bypass power
supply and connect to the power supply through a separate switch. Where a separated power source is not available, the
bypass and rectifier input supply connections are linked.
5.1.2 Static Transfer Switch
The circuit blocks labeled Static Switch in
fig.5-1
contain electronically controlled switching circuits that enable the critical
load to be connected to either the inverter output or to a bypass power source via the static bypass line. During normal
system operation the load is connected to the inverter; but in the event of a UPS overload or inverter failure, the load is
automatically transferred to the static bypass line. To provide a clean (no-break) load transfer between the inverter
output and static bypass line, the inverter output and bypass supply must be fully synchronized during normal operating
conditions. This is achieved through the inverter control electronics, which makes the inverter frequency track that of
the static bypass supply, provided that the bypass remains within an acceptable frequency window.
A manually controlled maintenance bypass supply is incorporated into the UPS design. It enables the critical load to be
powered from the utility (bypass) supply while the UPS is shut down for routine maintenance.
Note
When the UPS is operating in bypass mode or on maintenance bypass, the connected equipment is not protected
from power failures or surges and sags.
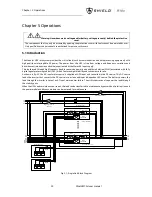
5.2 1+1 Parallel System
Several “single unit” UPS modules may constitute a “1+1” system, where up to two single units operate together for the
purpose of providing additional power or reliability or both. The load is equally shared between any paralleled UPSs.
5.2.1 Features of Parallel System
1. The hardware and firmware of single module UPS units are completely compatible with the requirements of a parallel
system. Parallel configuration can be achieved merely through settings in configuration software. The parameters
settings for the modules in parallel system shall be consistent.
2. Parallel control cables are connected in a ring, providing both performance and redundancy. Dual-bus control cables
are connected between any two UPS modules of each bus. The intelligent paralleling logic provides the user with
maximum flexibility. For example, shutting down or starting up UPS modules in a parallel system can be done in any
sequence. Transfers between Normal and Bypass modes of operation are synchronized and self–recovering e.g. following
overloads and their clearance.
3. The total load of the parallel system can be queried from each unit’s LCD.
5.2.2 Parallel Requirements of UPS Modules
A group of paralleled modules behave as if it were one large UPS with the advantage of presenting higher reliability. In
order to assure that all modules are equally utilized and to comply with relevant wiring rules, the following requirements
apply:
1. All UPS modules shall be of the same rating and must be connected to the same bypass source.
2. The bypass and the main input sources must be referenced to the same neutral potential.
3. Any RCD (Residual Current detecting device), if installed, must be of an appropriate setting and located upstream of
the common neutral bonding point. Alternatively, the device must monitor the protective earth currents of the system.
Refer to the High Leakage Current Warning in the first part of this manual.
4. The outputs of all UPS modules must be connected to a common output bus.
5. It is strongly recommended that each paralleled UPS install at least a redundant power module
Note
警告
危 险
警告
危 险
Summary of Contents for M10U
Page 1: ......
Page 9: ......
Page 71: ...Appendix B Power Connection of Modular System 62 Shield M10U user manual ...