47
Coordinate Conversions
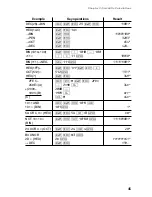
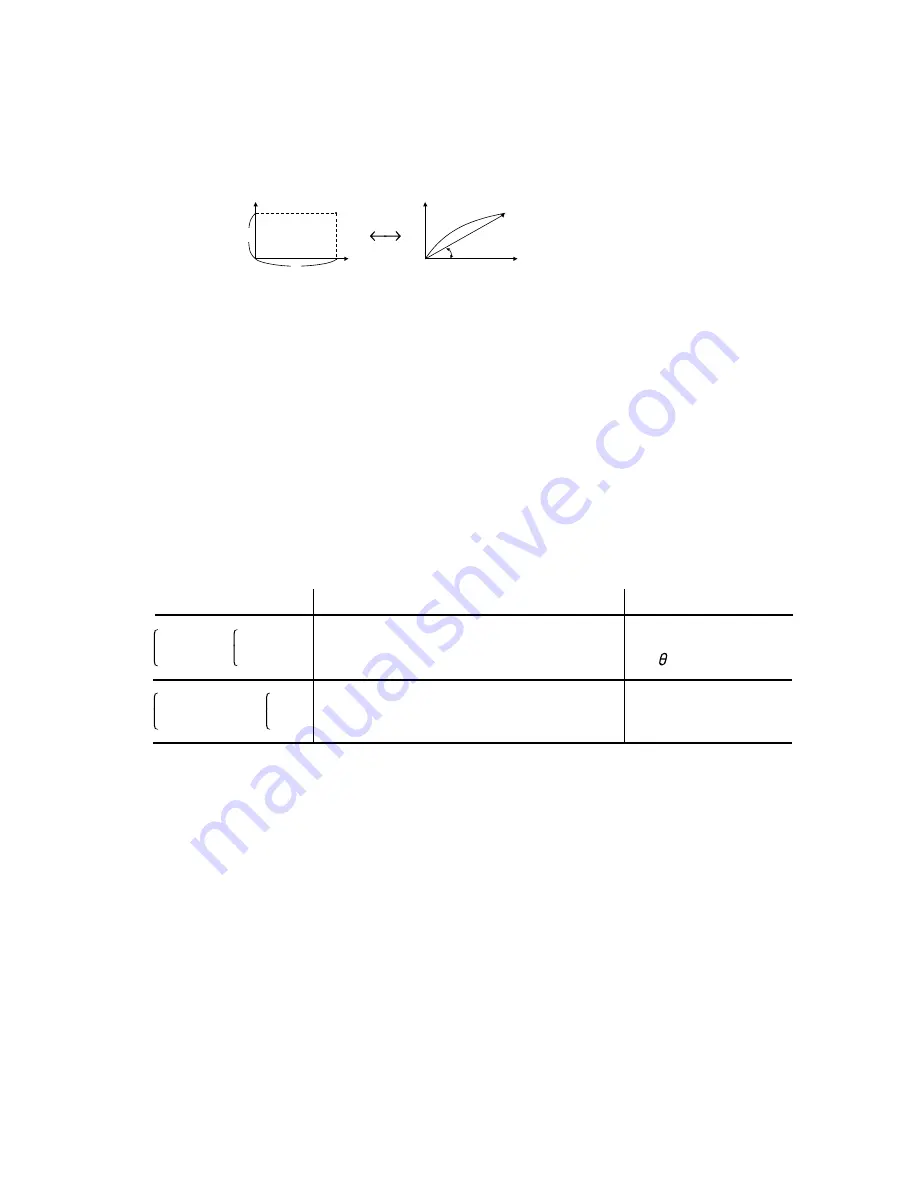
Conversions can be performed between rectangular and polar coordinates.
P (
x
,
y
)
X
Y
0
y
x
P (
r
,
θ
)
X
Y
0
r
θ
Rectangular coordinate
Polar coordinate
• Before performing a calculation, select the angular unit.
• The calculation result is automatically stored in memories.
• Value of
r
: R memory
• Value of
θ
:
θ
memory
• Value of
x
: X memory
• Value of
y
: Y memory
•
r
and
x
values are stored in the last answer memory.
j
6
,
4
x
= 6
→
r
=
@
u
r= 7.211102551
y
= 4
θ
= [
°
]
= 33.69006753
14
,
36
r
= 14
→
x
=
@
E
x= 11.32623792
θ
= 36[
°
]
y
=
y= 8.228993532
Example
Key operations
Result
Chapter 3: Scientific Calculations
Summary of Contents for EL-5230
Page 1: ...PROGRAMMABLE SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR OPERATION MANUAL EL 5230 EL 5250 ...
Page 2: ......
Page 12: ...10 ...
Page 62: ...60 ...
Page 132: ......