21
Using the solver function
You can solve any unknown variable in an equation by assigning known
values to the rest of the variables. Let us compare the differences between
the solver function and the simulation calculations using the same expres-
sion as in the last example.
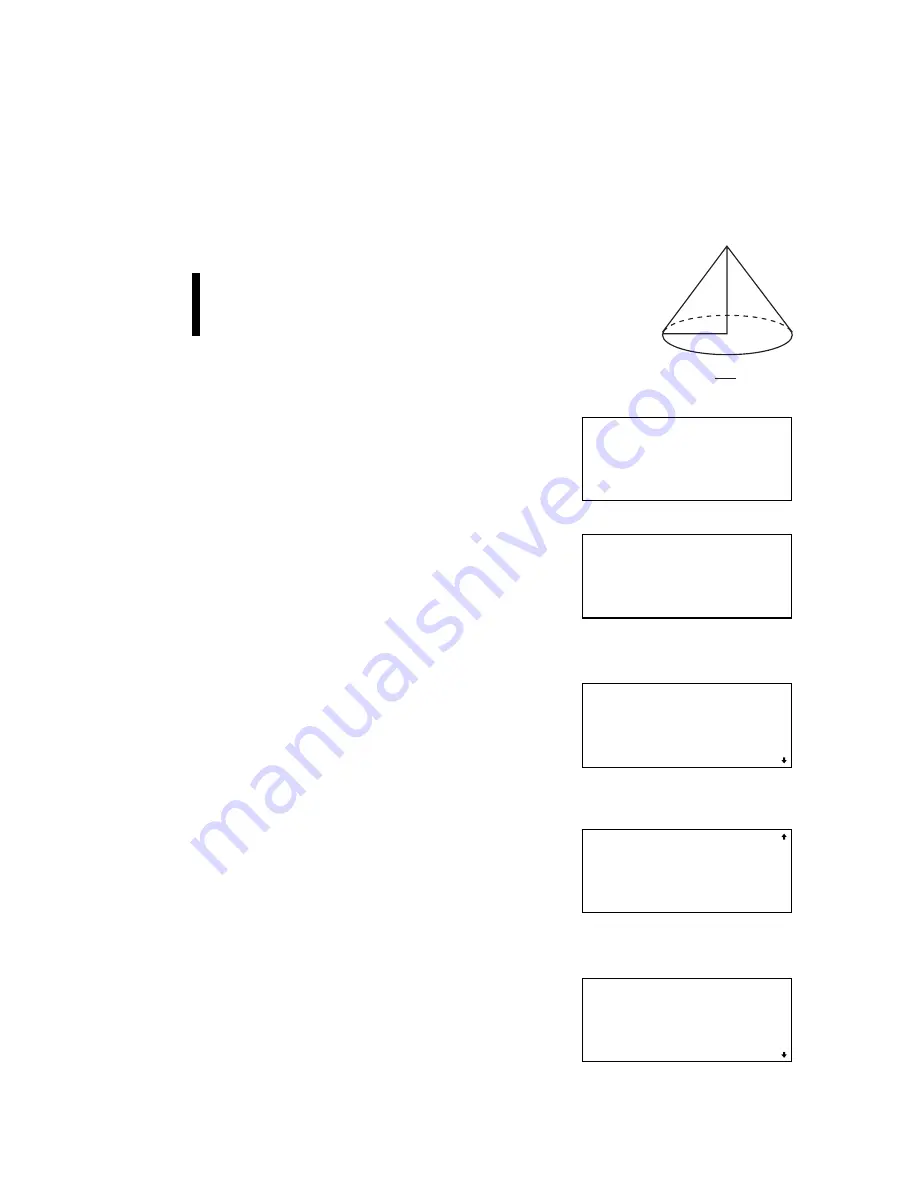
Example
What is the height of cone
3
if it has a radius of 8
and the same volume as cone
2
(r = 9, h = 8) in
the last example?
9.
Store the result of step 8 on the
previous page in variable V.
Press
j
twice and
;
<
x
V.
10. Input the equation (including ‘=’) in the
NORMAL mode.
Press
;
V
;
=
then input
the rest of the expression.
You must press
;
=
(
m
key), not
e
, to enter the = sign.
11. Press
I
5
to move to the
variable input display.
• Note that the values assigned to the
variables in the last example for the
simulation calculations are retained and
displayed.
12. Press
d
to skip the height, and
then press 8
e
to enter the radius
(R).
• The cursor is now on V. The value that
was stored in step 9 is displayed.
(volume of cone
2
)
13. Press
u
u
to go back to the
variable H.
• This time the value of H from memory is
also displayed.
V=1ı3πRŒH
H=z 8.
V=1ı3πRŒH
V=z678.5840132
AnsÒV
678.5840132
V=1ı3πRŒH_
2
V
=
π
r h
3
1
r
h
Chapter 1: Before You Get Started
0.
AnsÒV
678.5840132
V=1ı3πRŒH
H=z 8.
Summary of Contents for EL-5230
Page 1: ...PROGRAMMABLE SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR OPERATION MANUAL EL 5230 EL 5250 ...
Page 2: ......
Page 12: ...10 ...
Page 62: ...60 ...
Page 132: ......