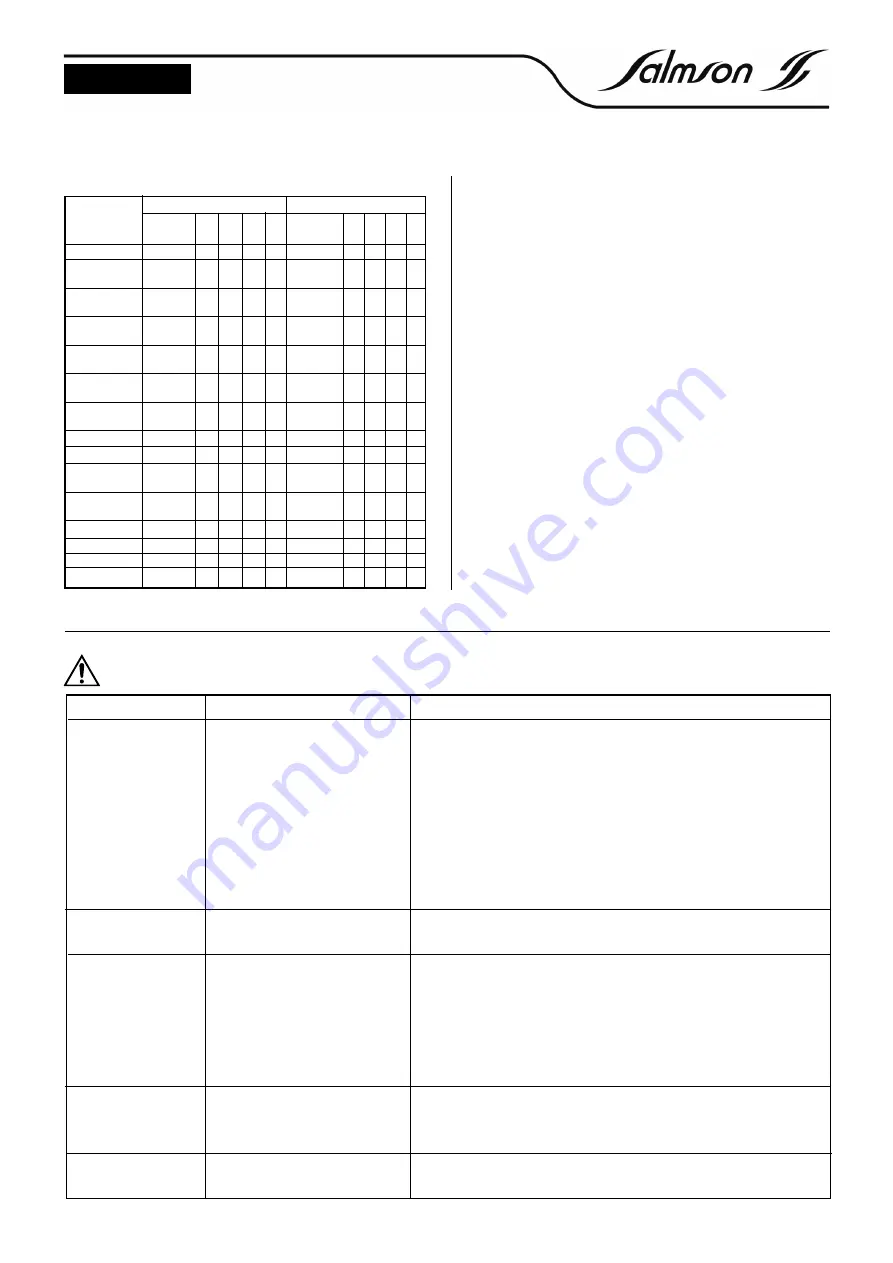
9
(1) or every 3 months - (2) every 6 months - (3) Descaling every 2 years if the
water is not treated.
Replacement frequency
1450 rpm
2900 rpm
Description
On each
1
2
3
5
On each
1
2
3
5
dismantling
year
years
years
years
dismantling
year
years
years
years
All gaskets
•
•
Front/rear
•
•
•
•
bearings
Impeller
•
•
key
Impeller nut
•
•
Lockwasher
Fabric
•
• (1)
packing
Mechanical
• (2)
seal
Shaft
•
sleeve
Shaft
•
•
Impeller closed
•
•
Pump screws
and bolts
•
•
Coupling catch
•
•
or spring
Bottom
•
•
Bearing
(3)
•
•
Circlips
•
•
•
Gland
•
•
8 . OPERATING TROUBLES
Switch the pumps OFF before doing any work on them.
TROUBLE
8.1 DIFFICULT PUMP PRI-
MING
8.2 THE PUMP DOES NOT
FLOW
8.3 FLOWRATE TOO LOW
(or not enough pressu-
re)
8.4 IRREGULAR PULSATORY
FLOWRATE
8.5 FLOWRATE TOO HIGH
CAUSE
a) Foot valve blocked or strainer clog-
ged:
b) Air penetration on suction pipe or at
flange gaskets of valves:
c) High point in the suction conduct, for-
ming air pockets:
d) Air penetration at the gland:
e) Pump not vented:
f) NPSH not complied with:
g) Speed too high in suction pipe:
h) Pumping of liquid containing air:
a) Valve closed on discharge:
b) The pump turns in reverse direction:
a) Valve on discharge partially open:
b) High head losses:
c) Motor-pump speed too low:
d) Conveyed products more viscous
than planned:
e) Suction pipe partially clogged or fou-
led:
a) Air or steam penetration:
a) Elevation height greater than plan-
ned, or pipe with too large a diameter:
REMEDY
a) Dismantle and rinse with jet.
b) No air penetration should be tolerated on this pipe: check all gaskets of flanges,
valves, plugs.
c) The pipe shall show ascending grade up to the pump (2 cm minimum per meter).
d) Re-tighten the gland evenly and check the injection connection.
e) Bleed by removing the pressure gauge plug.
f) Check it.
g) 1.5 m/s for liquids with low steam tension, 0.8 m/s for other products.
h) Review the installation.
a) Check and open it.
b) Reverse the direction of rotation by reversing 2 wires on the motor terminal block.
a) Open it progressively and fully until pressure is stable.
b) Check again the head losses (replaces pipes with other with larger diameter).
c) Wrong connection (star for triangle). Voltage too low: measure and reinforce the line
if necessary.
d) Get in touch with the manufacturer.
e) Check the pipe. Clean.
a) Perform methodical troubleshooting:
• on the suction pipe, check whether the strainer is well immersed to prevent the for-
mation of vortex,
• at the gland (braid) that should leak (drop by drop) when off, and motor-pump ope-
rating.
a) Reduce the flowrate through a diaphragm, by partial closing of the discharge valve or
by recycling.
ENGLISH


































