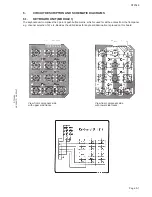
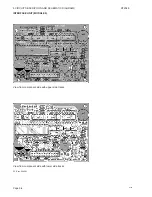
3.5.2.
ADJUSTMENT OF RX/TX UNIT
Alignment of Internal Power Supply
1.
Select channel 6.
2.
Select 1W output level and key the transmitter.
3.
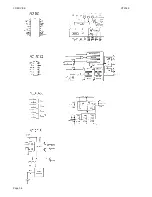
Connect a DC-voltmeter to the test point at the output of U01.
4.
Adjust the output voltage to 8V +50 mV by means of potentiometer R04.
Alignment of RF and IF Amplifier
1.
Select channel 6.
2.
Connect signal generator to antenna connector J04.
3.
Connect test probe to pin 16 on U03.
4.
Set signal generator frequency to 156.300 MHz and the output level to -30 dBm.
5.
Adjust transformers TR01, TR02, and coils L10, L11, L12, and L09 to maximum deflection on the
TP-meter.
Alignment of Detector and AF-Output Level
1.
Select channel 6.
2.
Connect signal generator to antenna connector J04.
3.
Connect frequency counter between pin 3 of U03 and frame through a 10 uF capacitor.
4.
Set signal generator level to -30 dBm (no modulation).
5.
Set signal generator frequency until frequency counter shows 450.0 kHz +100 Hz.
6.
Set modulation on signal generator to nominal modulation fm = 1 kHz, f = +3 kHz.
7.
Connect AF-voltmeter to the AF output at pin 11 on U03.
8.
Adjust coil L06 to maximum deflection on the AF-voltmeter.
9.
Adjust potentiometer R20 to 250 MVRMS ±10 MVRMS on AF-voltmeter.
10.
Connect distortion analyzer to the telephone output at pin 1 on P04.
11.
Make sure that distortion is minimum by slightly tuning transformer TR01.
12.
Check that distortion is below 5%.
Control of Receiver Sensitivity
1.
Select channel 6.
2.
Connect signal generator to antenna connector J04.
3.
Connect distortion analyzer to the telephone output at pin 1 on P04.
4.
Set signal generator to best sensitivity.
5.
Check that the sensitivity is better than 0.5 uV EMF for 12 dB SINAD.
6.
Repeat on channel 28.
Alignment of Transmitter Output Level
1.
Connect RF-power meter and a 50 ohm 25 Watt load resistor to antenna connector J04.
2.
Select channel 6 and key the transmitter.
3.
Adjust potentiometer R21 until the reading is 25 Watt.
4.
Set the output level to 1W.
5.
Adjust potentiometer R19 until the reading is 0.8 Watt.
3.6.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Troubleshooting should only be performed by persons with sufficient technical knowledge, who have the necessary
measuring instruments at their disposal, and who have carefully studied the operation principles and structure of
SAILOR RT2048.
The first thing to check is whether the fault is somewhere in the antenna circuit, the power source, the handset,
or in the transmitter - receiver unit.
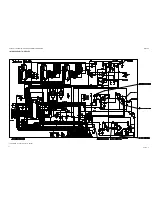
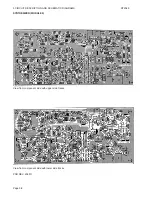
In order to help you during troubleshooting, the section 5. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION contains diagrams, principal
descriptions, and drawings showing the location of the individual components. Typical values for the DC and AC
voltages are indicated in the diagrams, and also the test points are indicated in the diagrams.
SAILOR RT2048 has a number of trimming cores and trimmers, which must not be touched unless adjustments
as specified in section 3.5. ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE can be made.
When measuring in the units, short-circuits must be avoided as the transistors would then be spoiled.
Page 3-3
Summary of Contents for RT2048 VHF
Page 1: ...INSTALLATION MANUAL SAILOR RT2048 VHF ...
Page 4: ......
Page 11: ...1 INTRODUCTION RT2048 Page 1 7 9403 BLOCK DIAGRAM ...
Page 12: ......
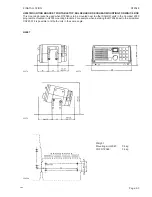
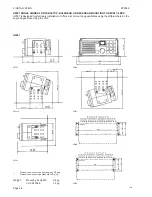
Page 22: ...2 INSTALLATION RT2048 Page 2 10 9346 626945 625473 ...
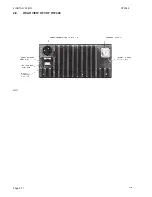
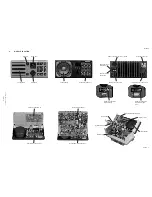
Page 24: ...2 INSTALLATION RT2048 2 8 REAR VIEW OF VHF RT2048 25567 9350 Page 2 11 ...
Page 26: ......
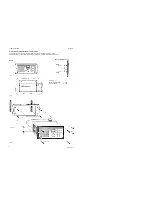
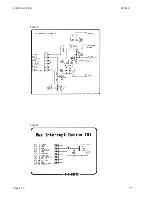
Page 31: ...3 Service RT2048 3 10 PIN CONFIGURATIONS Page 3 5 ...
Page 32: ...3 SERVICE RT2048 Page 3 6 ...
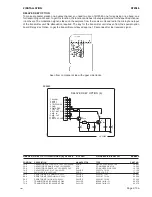
Page 33: ...3 Service RT2048 Page 3 7 ...
Page 34: ...3 SERVICE RT2048 Page 3 8 ...
Page 38: ...5 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION AND SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS RT2048 Page 5 2 ...
Page 89: ......
Page 90: ...Thrane Thrane A S info thrane com www thrane com M2048GB Issue E 0820 ...