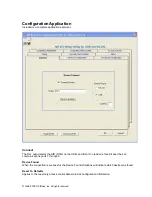
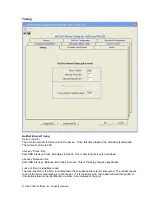
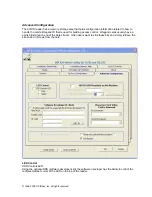
© 1996-2005 RF IDeas, Inc. All rights reserved
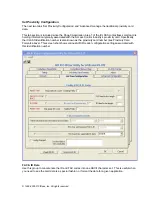
The ‘Get ID’ button may be pressed when the ‘Software Developer Kit Mode is checked (Advanced tab).
It is independent of configuration activity, except that it should not be called directly (within 1 second)
after performing a ‘Write’ to memory function.
When the user application is finished, the ‘Disconnect’ function should be pressed.
The ‘GetLibVersion’ function does not require that a ‘Connect’ be performed first. It only requires that
the Library DLL was successfully loaded into memory.
iCLASS Contactless Credentials
This section provides the developer with details about the HID iCLASS credentials. You will find more
details at HID’s web site located at
www.HIDCorp.com
.
Introduction to Application Areas
iCLASS
credentials:
•
iCLASS
, the most powerful read/write
contactless smart card available today,
features multiple memory sizes, form factor
options, and configurations.
•
All other application areas are open to
developer read/write data applications.
2kbits (256Bytes)
iCLASS
credentials:
•
The 2K is a highly secure credential optimized
for standard access control applications.
•
Application Area 2 is limited to 104 bytes of
read/write data. The key that secures the data
cannot be updated.
16kbits (2kBytes)
iCLASS
credentials:
•
The 16K is a highly modifiable, multi-
application credential with enough memory
area to store most common biometric
templates.
•
Application Area 2 of the 16K/2 credential
allows for 1896 bytes of read/write data, all of
which can be accessed with a single
authentication key.
•
The 16K credential can be configured for
either 2 or 16 application areas. Note: Once
configured, the credential cannot be
reconfigured.
•
The configuration block (block 1) of pages 1
through 7 on a 16K/16 credential is
modifiable. This allows for the additional
configuration of the Application Limit on these
pages.
Will my application fit on an
iCLASS
card? Use this table to find out.
Data Type
Size
(in bits)
Size
(in Bytes)
How many fit on
2kbits (256Bytes)
iCLASS
credential?***
How many fit on
16kbits (2kBytes)
iCLASS
credential?***
Yes/No (True/False)
1
1/8
832
15168
A single ASCII character
8
1
104
1896
A value less than 65535
16
2
52
948
RSI®
(Hand Geometry template)**
72 9
11
210
Bioscrypt®
(Fingerprint template)**
2784 348
0
5
LG/Iridian®
(Iris template)**
4096 512
0
3
Voice template*
10000
1250
0
1
Low-resolution photo*
12000
1500
0
1