© 1996-2005 RF IDeas, Inc. All rights reserved
Overview
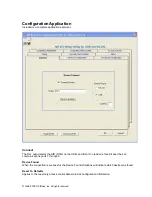
This document will guide the user through the various documents, specifications, and the contents of the
AIR ID Writer
Contactless Read/Write Smart Card Reader.
The
USB
and
RS-232
serial port contactless read/write reader are fully supported in an optional SDK
(software developer’s kit).
The
AIR ID Enroll
read-only reader may access only the serial number on the iCLASS contactless smart
card. No ability to write to the memory is supported with this reader.
NOTE: The Configuration Application, included at no charge, is for use with the reader/writer to
demonstrate the AIR ID features and functionality. RF IDeas offers a SDK (software developer’s
kit) for third party software developers to develop more serious applications around the AIR ID
platform.
iCLASSAPI.DLL
The
-USB
and
RS-232
uses drivers supplied with the operating system, however there is a DLL library
required that is supplied by RF IDeas. The configuration application makes use of this DLL,
"iClassAPI.dll"
, which is required for use with the device.
The file: "iClassAPI.dll" is the DLL that manages all operations necessary to:
1. Read and Write device configuration items and retrieve a card ID when a card is presented to
the reader,
2. It also provides a means to program HID iCLASS smart cards with application data and read it
back, and
3. To change master keys in the reader and cards.
The reader’s configuration items are grouped according to their general function and are handled
through structures defined in this document.
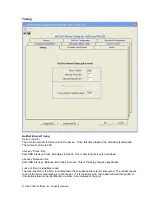
Before the configuration items are accessible, the application must be instructed to ‘Connect’ to the
device and told to ‘Read’ all configuration items. Once the items have been read into local storage, the
user may then access them through the four groups of ‘Get’ and ‘Set’ functions. The configuration items
are sent back to the device for permanent storage only when the ‘Write’ function is called.
The device may be reset to factory default values by pressing ‘Reset to Defaults’ under the Connect tab.
This is a fast method to bring the device to a known state.
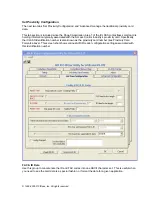
To read an ID from an iCLASS card/token, it is only necessary to ‘Connect’ to the device. No
configuration is necessary if the user is confident that the device is already configured appropriately.
The majority of the discussion within this document will be focused on using the AIR ID reader with HID
iCLASS contactless smart cards.
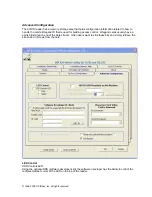
The iCLASS cards have two primary areas for the user to work with:
•
Read-Only card data, typically known as proximity card data used in the building access control
world. This information is held in Page 0, Application Area 1 with secure keys known only to
HID. There are several ‘configuration parameters associated with this data that may be saved
within the reader.
•
Read/Write card data that is held in Application Areas 2 and above.