26
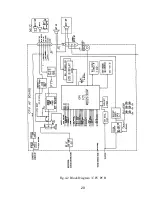
4.1.5 Low Frequency Circuit:
The low frequency signal re-modulated by IC307 obtains -6dB/oct characteristic
by going through the de-emphasis circuit which contains BUFF (IC13A) and
LPF (Q25). Then the signal is input to the low frequency section of CPU AF
board.
4.1.6 Squelch Circuit:
If no signal is input to the antenna, noise signal is amplified by the amplifier (IC
13B), As the result of receiving the amplified noise signal, the squelch circuit of
IC307 outputs BUSY signal. Squelch level is controlled by VR101.
4.1.7 Low Frequency Treatment Circuit (CPU AF Board):
The re-modulated low frequency signal is amplified in AMP (Q7). Its volume
can be adjusted by the tone volume (VR 102).
BUSY signal, output from the squelch circuit (6), becomes a MUTE signal after
being conditioned in CPU circuit. The low frequency signal is turned on and off
by the transistor switch (Q6) which is driven by this MUTE signal.
The low frequency signal further undergoes power-amplification in the low-
frequency-power-amplifier (IC 305) to drive the speaker. With the amplifier
circuit (IC6, Q8, Q10), which drives the microphone speaker, it is possible to
monitor the receiving tone heard from the microphone speaker. This driving
circuit can be turned on and off by key operation.
4.1.8 WX Alert Detection:
The tone selector (IC10 RF Board) detects the 1050Hz alert tone if it is
contained in the re-modulated receiving signal. The operating mode is changed
to WX receiving mode when CPU confirms that the alert tone has been detected.
4.2 TRANSMITTING CIRCUIT OPERATION
4.2.1 Microphone Amplifier Circuit:
Voice signal from the microphone is amplified by TX MIC AMP (IC5AJC5B)
in the CPU AF Board. At the same time, the voice signal obtains pre-emphasis
characteristic of 6 dB/oct in the range from 300Hz to 3KHz. The oscillation
width of this signal is limited by LIMITER circuit (D5) of the RF board. The
harmonic wave distortion generated by this oscillation width limitation is
removed by TX MOD LPF (IC31). Then the voice signal is input to VCO
section of PLL circuit as a modulation signal. This modulation signal frequency
is modulated directly by the variable capacity diode D11 of VCO.
Summary of Contents for RAY 210VHF
Page 2: ......
Page 3: ......
Page 4: ......
Page 6: ......
Page 8: ......
Page 10: ......
Page 12: ......
Page 19: ...7 Figure 2 2 Outline and Mounting Dimensions...
Page 30: ...18 Figure 3 1 Layout of Controls and Connectors...
Page 40: ...28 Fig 4 1 Block Diagram RF PCB...
Page 41: ...29 Fig 4 2 Block Diagram CPU PCB...
Page 55: ...43 6 2 RAY210 ASSEMBLY DRAWING...
Page 57: ...45 6 3 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM Fig 6 1 Schematic diagram RF PCB...
Page 58: ...46 Fig 6 2 Schematic diagram CPU PCB l...
Page 59: ...47 Fig 6 2 Schematic diagram CPU PCB 2...
Page 60: ...48 Fig 6 3 RF PCB Layout Top View...
Page 61: ...49 Fig 6 4 RF PCB Layout Rear View...
Page 62: ...50 Fig 6 5 CPU PCB Layout Top view...
Page 63: ...51 Fig 6 5 CPU PCB Layout Rear View...
Page 64: ...52...
Page 75: ...63...