4 . 1 Recording
4 . 1 . 1 Automatic gain control ( A G O
A clamper fixes the sync tip level and makes the video sig
nal amplitude constant.
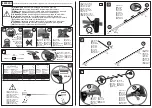
Recording
h3
Freq.
converter
/ s : 3.58MHz
carrier
Video
out
Deviation
yiMHz]
Down-converted
C-signal
Fig. 13 Simplified Block Diagram of VCR
Supersonic w a v e
lb) Delay-line
C-component
7
Filters
Y - c o m p o n e n t
Filters
C-component
(c) Characteristic
Fig. 14 Y-C Separation by Comb Filter
4 . 1 . 3 Y-signal emphasis
White noise is unavoidable in F M . T h e noise level of this
kind increases in proportion t o frequency. The noise, there
fore, is suppressed by preemphasis before modulation a n d
deemphasis after d e m o d u l a t i o n . 8 m m V C R a n d 1/2"
VCRs in
0
I I & III and V H S E P modes employ the dynamic
emphasis system by which the a m o u n t of emphasis is
decreased as the input signal level increases t o prevent over-
m o d u l a t i o n . T h e Y-signal is then clipped a n d F M e d .
36
4 . 1 . 2 Y-C separation
T h e Y- a n d C-signals are separated by Y-C separator t o
avoid intermodulation distortion because they have been
in t h e same frequency b a n d .
T h e input signal is added to or subtracted from the 1H-
delayed signal. The addition and subtraction yields Y- a n d
C-signals respectively because of t h e phase difference be
tween adjacent lines (NTSC). Ref. Fig. 2, p l 3 .
Playback
FMed Y-signal
Y
Y
AGC
LPF
BPF
ACC
C-signal
Video
input
FM
modulator
HPF
LPF
urn
A m p
Leve
l
Bandwidth
FMed Y-signal
HPF
LPF
Freq.
demodulator
Freq.
converter
LPF
BPF
Mix
Y
:C
1H
(63.5/is)
delay
Vd
In
Vi
Y o u t
C out
(a) Circuit
Silica
Piezoelectric
element
O u t p u t
Input
Piezoelectric
element
Y - c o m p o n e n t
Amplitud
e
Emphasi
s
(dB
)
Vide
o
inpu
t leve
l (dB
)
For weak signal
For strong signal
Frequency (MHz)
Fig. 15 An Example of Dynamic Preemphasis
i/3)