EV Charge Control Basic
26 / 68
PHOENIX CONTACT
106377_en_04
5.4
Vehicle status (status A - F)
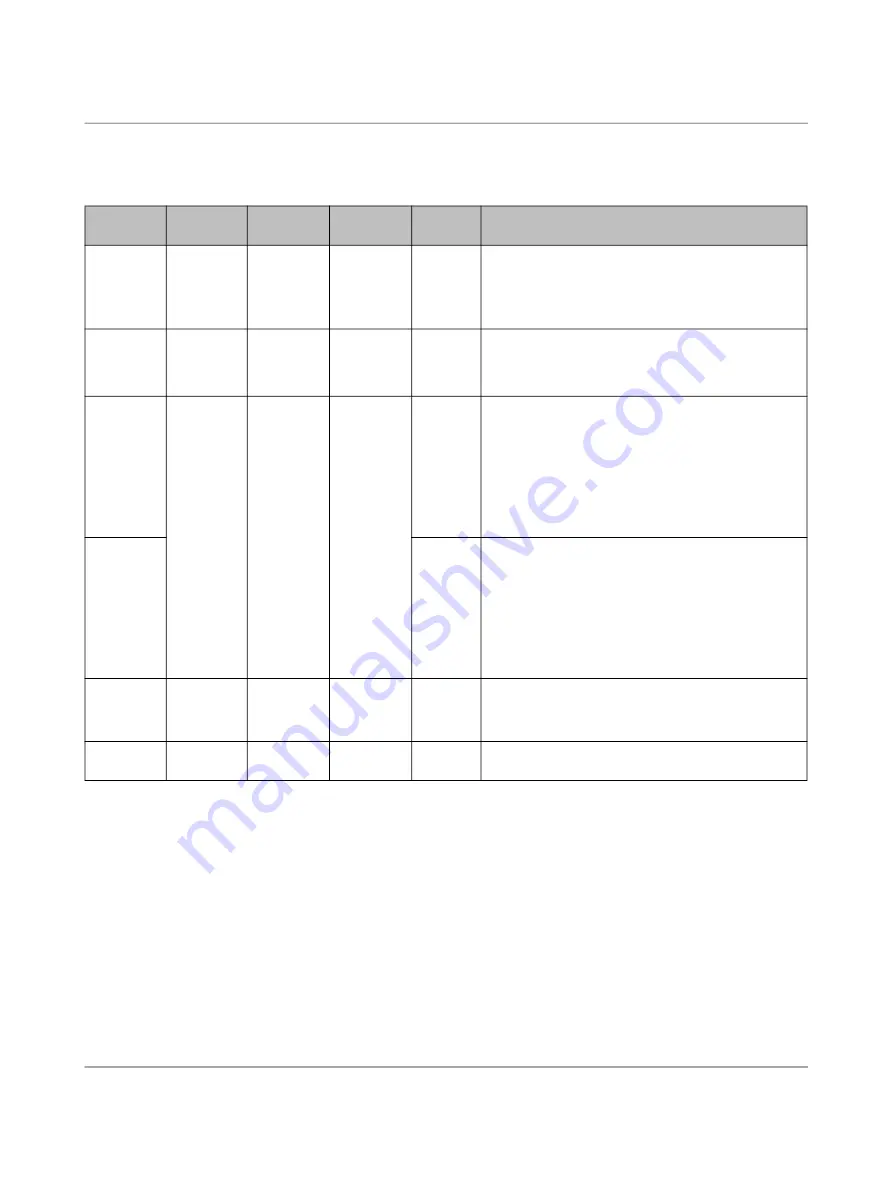
Table 5
-
3
Vehicle status according to IEC 61851-1
Vehicle
status
Vehicle
connected
S2
*
Charging
possible
Va
†
Description
A
No
Open
No
12 V
Vb
‡
= 0 V
A1
(12 V DC): No vehicle connected
A2
(12 V PWM): Only temporary transition state,
enters the A1 state
B
Yes
Open
No
9 V
R2 detected
B1
(9 V DC): EVSE
**
not ready yet
B2
(9 V PWM): EVSE ready
††
C
Yes
Closed
Vehicle
ready
6 V
R3 = 1.3 kΩ ±3%
Ventilation not required
C1
(6 V DC): EVSE not ready, charging process
aborted. Transition state; possible as a perma
-
nent state only in the event of a simplified
Control Pilot.
C2
(6 V PWM): Charging process active
D
3 V
R3 = 270 Ω ±3%
Ventilation of the charging area required
D1
(6 V DC): EVSE not ready, charging process
aborted. Transition state; possible as a perma
-
nent state only in the event of a simplified
Control Pilot.
D2
(6 V PWM): Charging process active
E
Yes
Open
No
0 V
Vb = 0: EVSE
Mains problem or mains not available, short circuit on
the Control Pilot
F
Yes
Open
No
EVSE not
available
EVSE not available
*
Switch S2 (see
“Control Pilot wiring” on page 24
)
†
Va = measured voltage in the EV Charge Control Basic
‡
Vb = measured voltage in the vehicle
**
EVSE = Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (charging station)
††
The charging station can be set to an operational state using a signal at the Enable input, or the relevant Modbus command.
Summary of Contents for EV Charge Control Basic
Page 1: ...User manual EV Charge Control Basic Installing and starting up the charging controller ...
Page 14: ...EV Charge Control Basic 14 68 PHOENIX CONTACT 106377_en_04 ...
Page 34: ...EV Charge Control Basic 34 68 PHOENIX CONTACT 106377_en_04 ...
Page 46: ...EV Charge Control Basic 46 68 PHOENIX CONTACT 106377_en_04 ...
Page 69: ......
















































