Circuit Descriptions and Abbreviation List
9.
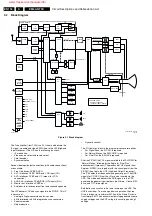
The RGB amplifiers on the CRT-panel are supplied with 200 V
from the LOT.
The Auto-SCAVEM circuit modulates transitions of the
Luminance (Y) signal on the horizontal deflection current,
giving a sharper picture.
The sound part is built around the MSP34x2 (Multi-channel
Sound Processor) for IF sound detection, sound control and
source selection. Dolby decoding is also done by the MSP.
Amplification is done via a 'class D' integrated power amplifier
IC, the TDA7490.
The microprocessor, called OTC (OSD, TXT/CC and Control)
takes care of the analog CC input processing and output
processing. The OTC, ROM, and RAM are supplied with 3.3 V,
which is derived from the +5V2.
The NVM (Non Volatile Memory) is used to store the settings,
the Flash-RAM contains the set software.
There is a separate Standby Supply, in order to reduce the
Standby power consumption. During Standby, the Main Supply
is switched 'off' (via TS7529.)
A relay (1550) is used to switch the Degaussing circuit. It is
switched 'on' after set start-up and switched 'off' by the
µ
P after
12 s.
The Main Supply, a SMPS based on the 'boost-converter'
principle, generates the 141 V (V
BAT
) and the +/- 16 V for the
audio part.
Note: Voltage V
BAT
is not mains isolated ('hot'), but is alignment
free.
9.3
Power Supply (Diagram A1 and A2)
The power supply has a number of main functions:
1.
Mains harmonic filter.
2.
Degaussing picture tube.
3.
Standby power supply.
4.
Main supply.
9.3.1
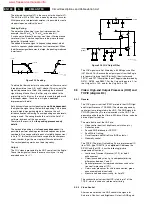
Mains Harmonic Filter (Diagram A1)
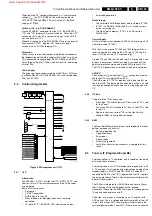
Figure 9-2 Mains harmonic filter circuitry.
The mains harmonic filter has two functions: to prevent high
frequency signals (harmonics) from being transferred into the
mains and to protect the set from lightning damage.
C2507 prevents the high frequency signals generated by the
set, from being conveyed into the mains (it forms a short-
circuit.)
In case of a lightning surge between the 2 phases (differential
mode), the energy is immediately bled away through the VDR
(R3509) to the other phase.
In case of a lightning surge on both phases of the mains in
relation to the aerial earth (common mode), the filter acts as a
high resistance (U
EMK
= L * dI/dt), as a result of which the
voltage across coil L5503/04 increases. A spark gap (1590)
prevents the voltage from increasing too much, which would
lead to a damaged coil. When ignited, the current will be
discharged via this spark gap.
Resistor R3500 is used for limiting the inrush-current.
9.3.2
Degaussing (Diagram A1)
As soon as the set is switched 'on' via the ON/OFF switch, the
5V2 is present. When the 'DEGAUSSING' signal from the
processor (OTC) is 'low,' transistor 7528 will conduct, and relay
1550 is activated. Initially a considerable current will flow, via
PTC 3516, through the degaussing coil. The PTC will heat up,
resistance will rise, and the current will decay rapidly. The OTC
makes the 'DEGAUSSING' signal 'high' after 12 s, which will
switch 'off' the relay.
9.3.3
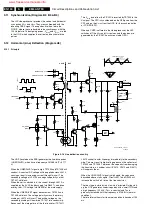
Standby power supply (Diagram A2)
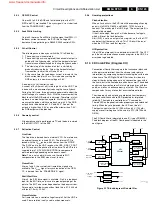
Principle
This power supply is not only delivering the standby voltage,
but also the main voltages for the small signal part. It is a SOPS
type (Self-Oscillating Power Supply) and is regulated by the
controlled switching of an oscillator. It uses the 'Flyback'
principle:
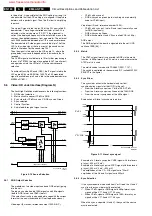
Figure 9-3 Flyback principle
After closing switch 'S,' the current I
D
will increase linear in time.
The magnetic energy in the primary coil is directly proportional
with the self-inductance of the coil and current I
D
(thus with the
time the switch is closed.)
The voltage polarity at the secondary winding is negative (due
to different winding direction), meaning that diode D will block.
Capacitor C will discharge via R
L
, and U
OUT
will decrease.
Opening switch 'S' will generate a counter-e.m.f. in the primary
winding, trying to maintain current I
D
. Through this the polarity
of the secondary voltage will inverse. The magnetic energy
stored in the coil, will now be transformed to the secondary
side. Diode D will now conduct, capacitor C will be charged and
U
OUT
will increase.
CL 16532044_020.eps
140501
2507
mains
3521
4M7
1501
1590
3501
9503
Mains harmonic
diversity
3551
2
1
3
4
V
9504
9504
+375V
-
-
+
2516
2537
3500
5502
5511 or 5516
3
1
1
2
4
3
2
5503 or
5504
96532156_020.eps
210100
+
-
-
+
-
-
+
+
RL
D
Id
Uout
C
+
C
+
375V
S
RL
D
Uout
375V
S
Isec
www.freeservicemanuals.info
Summary of Contents for EM5A NTSC
Page 6: ...Direction for Use EN 6 EM5A NTSC 3 3 Direction for Use www freeservicemanuals info ...
Page 7: ...Direction for Use EN 7 EM5A NTSC 3 www freeservicemanuals info ...
Page 8: ...Direction for Use EN 8 EM5A NTSC 3 www freeservicemanuals info ...
Page 9: ...Direction for Use EN 9 EM5A NTSC 3 www freeservicemanuals info ...
Page 10: ...Direction for Use EN 10 EM5A NTSC 3 www freeservicemanuals info ...
Page 11: ...Direction for Use EN 11 EM5A NTSC 3 www freeservicemanuals info ...
Page 12: ...Direction for Use EN 12 EM5A NTSC 3 www freeservicemanuals info ...
Page 13: ...Direction for Use EN 13 EM5A NTSC 3 www freeservicemanuals info ...
Page 14: ...Direction for Use EN 14 EM5A NTSC 3 www freeservicemanuals info ...
Page 15: ...Direction for Use EN 15 EM5A NTSC 3 www freeservicemanuals info ...
Page 16: ...Direction for Use EN 16 EM5A NTSC 3 www freeservicemanuals info ...