Page 31
Ph: 804.227.3023
10511 Old Ridge Rd. Ashland, VA 23005
4LHD/4LHDX Application Manual
Powertrain Control Solutions
REV 1.1
2.2 Transmission Output
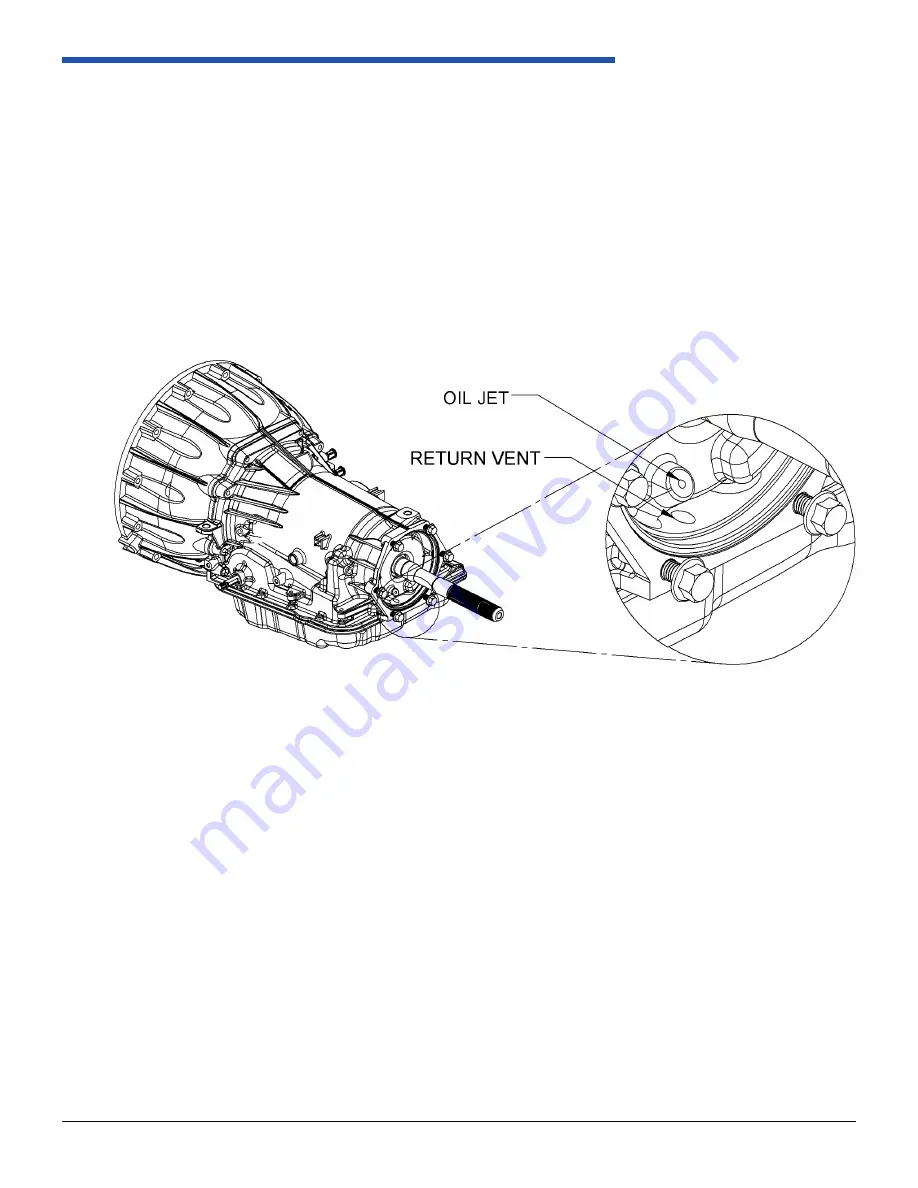
2.2.1 Lubrication and Sealing
Referenced in Figure 2.2.1-1 is the lubrication system for all 4LHD/4LHDX extension housings. This system
ensures the spline engagement, rear bearings, and seals retain optimal functionality for the life of the transmission.
It is critical that the extension housing is properly sealed from the environment and transfer case oil. Fluid enters
the cavity from both the oil jet and output shaft bearing, and drains to the oil pan through the return vent. PCS uses
a universal extension housing to transmission seal. The seal between the transmission case and the extension
housing is referenced in Figure 2.2.3-4. During transmission operation the return vent must not be plugged, as
this will cause the extension housing to fill with fluid which can cause permanent damage. Contact PCS in the
case of applications requiring dry extension housings.
2.2.2 Output Shaft Requirements
Propshaft Alignment and Torsional Vibrations
The presence of universal joints in the propshaft will induce torsional vibrations in the driveline, due to the angles
at which the driveshafts operate. This can have a detrimental effect on component durability.
The chassis shall be designed to minimize the torsional vibration resulting from excessive driveshaft angle. Refer
to
SAE Design Guideline AE-7: Universal Joint and Driveshaft Design
. Excitations in the driveline, during any
continuously operating condition, shall not exceed:
Torsional excitation:
400 rad/s2
Inertia excitation:
1000 rad/s2
If a design approaches or exceeds these criteria, or if a design is considered at risk, a test shall be conducted to
ensure that the transmission is not compromised. This information can be found in the
SAE Design Guide Line
AE-7: Universal Driveshaft Design
.
Figure 2.2.1-1: Extension Housing Fluid Control
















































