- Eng-18 -
English
Cooking Techniques
FOOD CHARACTERISTICS
Food characteristics which affect conventional cooking are
more pronounced with microwave heating.
Size
–– Small portions cook faster than large ones.
Shape
–– Uniform
sizes heat more
evenly. To
compensate for
irregular shapes,
place thin pieces
toward the centre of
the dish and thicker
pieces toward the edge of dish.
Starting Temperatures
–– Room temperature foods take
less time to heat up than refrigerator frozen foods.
Bone and Fat
–– Both
affect heating. Bones
may cause irregular
heating. Large
amounts of fat absorb
microwave energy and
meat next to these
areas may overcook.
Density
–– Porous, airy foods take less time to heat than
heavy, compact foods.
Timing
A range in heating time is given in each recipe. The time
range compensates for the uncontrollable differences in
food shapes, starting temperature and regional preferences.
Always cook food for the minimum cooking time given in the
recipe and check for doneness. If the food is undercooked,
continue cooking. It is easy to add time to an undercooked
product. Once the food is overcooked, nothing can be done!
Spacing
Individual foods, such as baked potatoes, cupcakes and
hors d’oeuvres, will heat more evenly if placed in the oven
equal distance apart.
When possible, arrange
foods in a circular pattern.
Similarly, when placing foods in a baking dish, arrange
around the outside of dish, not lined up next to each other.
Food should NOT be
stacked on top of each
other.
Piercing
The skin or membranes on some foods will cause steam to
build up during microwave cooking. Foods must be pierced,
scored or have a strip of skin peeled off before cooking to
allow steam to escape.
Eggs:
Pierce egg yolk twice and
egg white several times
with a toothpick.
Whole Clams and Oyster:
Pierce several times with a toothpick.
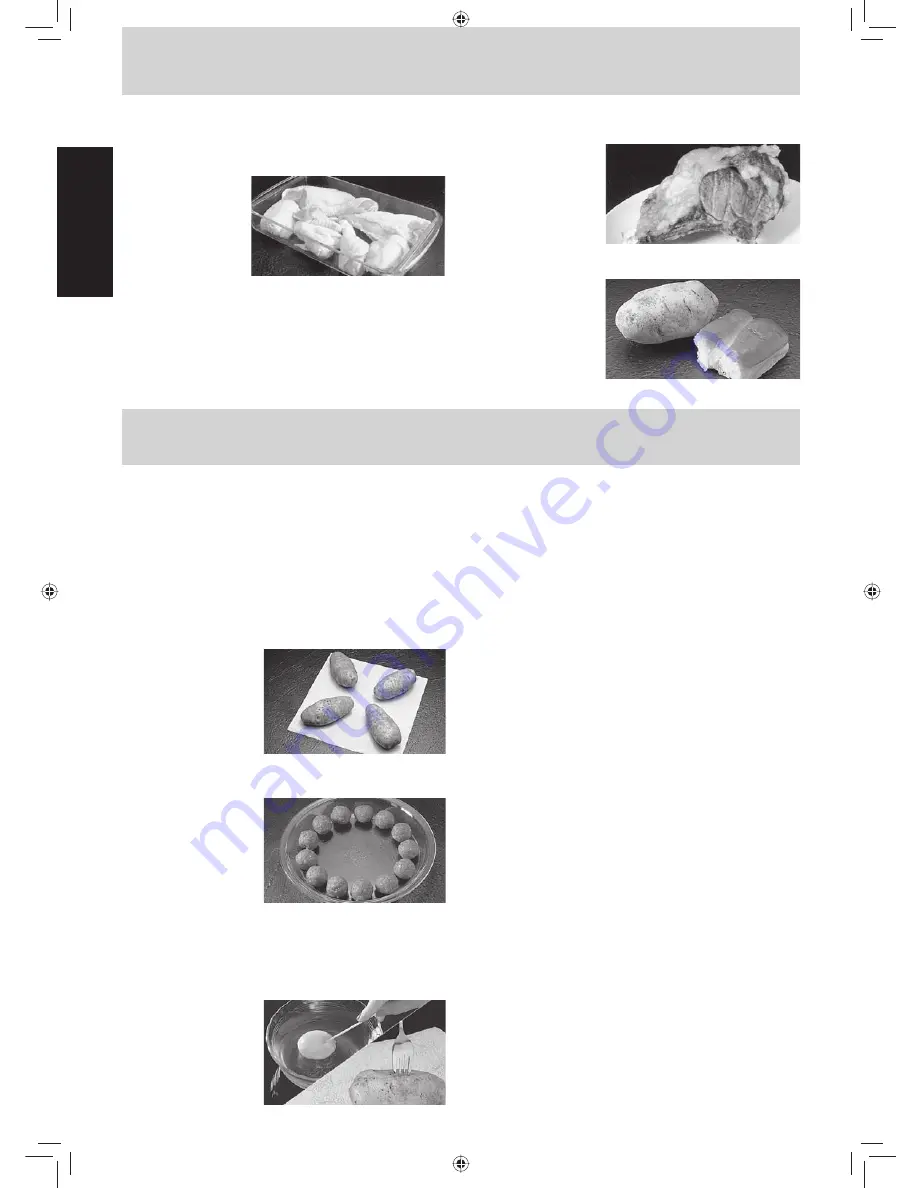
Whole Potatoes and Vegetables
: Pierce with a fork.
Frankfurters and Sausages
: Score smoked polish
sausage and frankfurters. Pierce fresh sausage with a fork.
Browning
Foods will not have the same brown appearance as
conventionally cooked foods or those foods which are
cooked utilizing a browning feature. Meats and poultry may
be coated with browning sauce, Worcestershire sauce,
barbecue sauce or shake-on browning sauce. To use,
combine browning sauce with melted butter or margarine;
brush on before cooking.
For quick breads or muffins, brown sugar can be used in the
recipe in place of granulated sugar, or the surface can be
sprinkled with dark spices before baking.
Covering
As with conventional cooking moisture evaporates during
microwave cooking. Because microwave cooking is done by
time and not direct heat, the rate of evaporation cannot be
easily controlled. This, however, can be easily corrected by
using different materials to cover dishes. However, unless
specified, a recipe is heated uncovered. Casserole lids or
cling film are used for a tighter seal. Various degrees of
moisture retention are also obtained by using wax paper or
paper towels.
Stirring
Stirring is usually necessary during microwave cooking. We
have noted when stirring is helpful, using the words once,
twice, frequently or occasionally to describe the amount of
stirring required. Always bring the cooked outside edges
toward the centre and the less cooked centre portions
toward the outside.
Food Characteristics
IP3914_3BB22HP_Eng_05_120625.indd Sec1:18
IP3914_3BB22HP_Eng_05_120625.indd Sec1:18
2012-6-25 10:26:11
2012-6-25 10:26:11



















