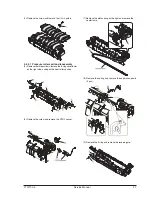
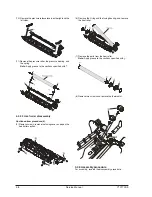
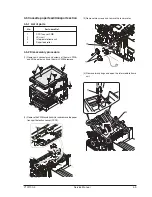
Y101700-5
Service Manual
3-3
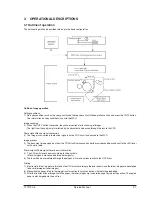
3.3 Laser unit
The image data sent from the MCU (image process
circuit) is sent to the LSU (laser unit), where it is converted
into laser beams.
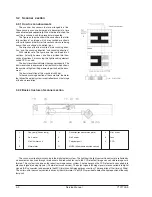
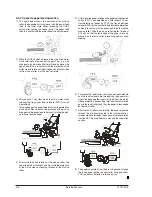
3.3.1 Basic structure
The LSU unit is the writing section of the digital optical
system. The semiconductor laser is used as the light source,
and images are formed on the OPC drum by the polygon
mirror and f
θ
lens, etc. The laser beams are passed through
the collimator lens, the cylindrical lens, the polygon mirror,
the f
θ
lens, and the mirror to form images on the OPC drum
in the main scanning direction. The laser emitting PWB is
provided with the APC (auto power control) in order to
eliminate fluctuations in the laser power. The BF PWB
works for measurement of the laser writing start point.
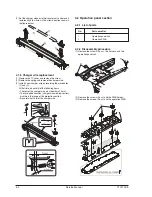
No.
Component
Function
(1)
Semiconductor laser
Generates laser beams.
(2)
Collimator lens
Converges laser beams in
parallel.
(3)
Polygon mirror,
Reflects laser beams at a
polygon motor
constant rpm.
(4)
BD (Mirror, lens, PWB)
Detects start timing
of laser scanning.
(5)
f
θ
lens
Converges laser beams at
a spot on the drum.
Makes the laser scanning
speeds at both ends of
the drum same as each
other
(refer to the
figure below).
Makes the laser scanning speeds at both ends of the drum
same as each other.
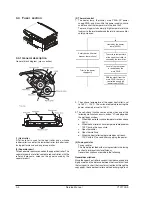
3.3.2 Laser beam path
3.3.3 Composition
Effective scanning width:
216mm (max.)
Resolution:
600dpi
Beam diameter:
75um in the main scanning
direction, 80um in the sub
scanning direction
Image surface power:
0.20 ±0.03mW (Laser
wavelength780 – 795nm)
Polygon motor section:
Brushless motor 20.787rpm
No. of mirror surfaces: 6
surfaces
Laser beam
path for BF PWB