10 How the C-Quant works
32 / 56
Instruction Manual C-Quant ( G/80000/1007/en)
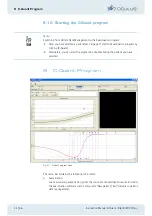
The psychometric function can be used to determine a person’s straylight value with
great precision on the basis of only a few stimuli responses.
Rather than by determining the straylight value "directly" this is done by finding the point
on the curve where the response value becomes 0.5.
In our example this happens at two points: one where both test fields are switched off
and one where the compensation light is precisely twice a intense as the scattered light.
At the second point the curve shows a very steep slope.
The goal is to locate this point, also referred to as the 50 % value.
The patient responses will normally change quickly in the proximity of the 50 % value re-
sulting in the steep slope at this point.
From here the patient’s straylight value can easily be calculated.
Results obtained in this way have shown to be very precise and reproducible.
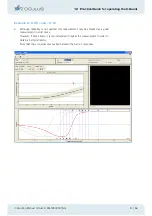
10.4 Strategy details
In practice the examination procedure is a little more complicated.
Stimuli are presented left and right at random to prevent the patient’s anticipation from
influencing the outcome.
Also, to prevent the patient from confusing differences in flicker intensity with differenc-
es in brightness, the instrument continually adjusts the test fields so that they have equal
average brightness at each presentation.
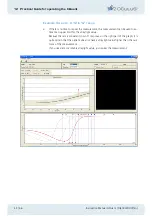
The abscissa of the examination response chart has a logarithmic scale, termed "straylight
compensation level log(s)".
The "straylight compensation level" is determined by the ratio between the compensation
light (in one half of the central test field) and the intensity of the straylight source. It is
given in the same measurement units as the straylight parameter "s".
In this way the responses given by the patient can be assessed directly in terms of his
straylight value.
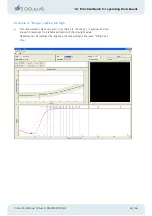
With a logarithmic scale the response pattern (probabilities according to the psychome-
tric function) takes on a constant shape when depicted graphically.
To determine the patient’s straylight value the psychometric curve is shifted horizontally
until it most closely fits with the response pattern.
The patient’s 50 % value is exactly twice as high as his straylight value.
10.5 Examination phases
Instruction phase
This phase is available as an option to familiarize the patient with the examination pro-
cedure.
It consists of five stimuli which do not contribute to the examination outcome.
The first three stimuli are presented without the straylight source, i.e. the flicker is pro-
duced only by the two test fields.