10 How the C-Quant works
30 / 56
Instruction Manual C-Quant ( G/80000/1007/en)
.
During the examination a number of short stimuli are presented to the patient and he is
then asked to decide which of the two test fields flickers more intensely.
The following example illustrates the underlying idea.
The left test field is off all the time.
In the right test field compensation light appears counter-phase to the straylight source
at varying intensity.
We will assume that patient has a straylight value of 10. The dimensional unit of stray-
light is disregarded in this example because it has no significance for understanding the
measurement principle.
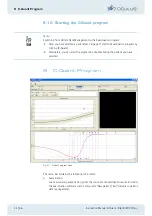
Seven stimuli for the compensated field are shown:
Fig. 10-2: Seven stimuli
The left test field corresponds to stimulus numbher 3 all the time.
If the patient states that the left test field flickers more intensely, this is counted as "0".
If he sees the right test field flicker more intensely, this gives "1".
For the individual stimuli this has the following consequences:
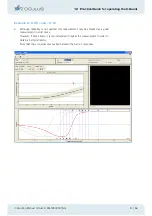
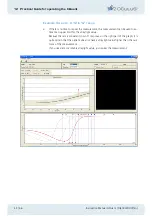
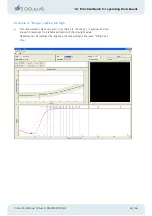
1
Here no compensation light is presented, so that the two test fields appear the same.
Given sufficient test repetition the patient will choose right just as often as left, giv-
ing an average value of 0.5.
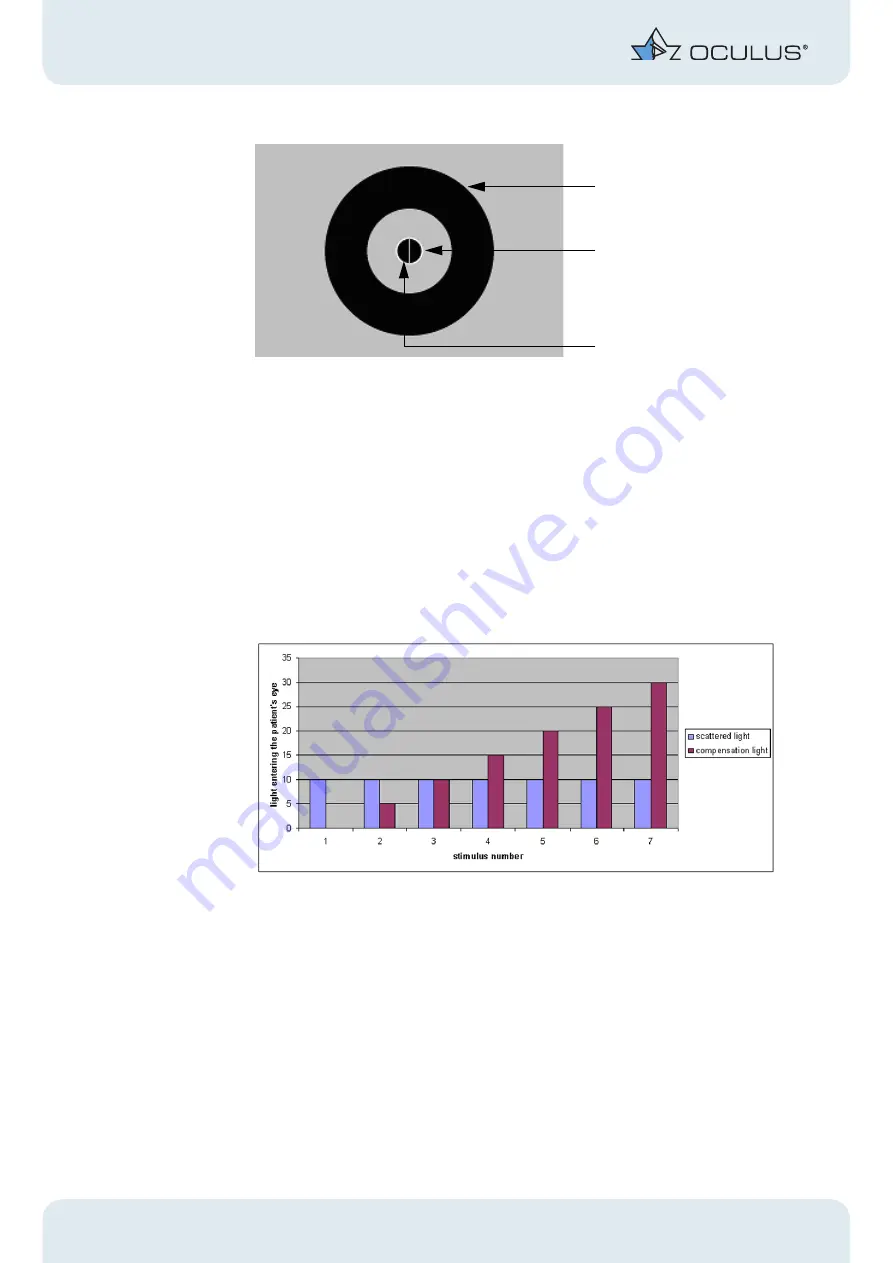
straylight source (outer ring)
right test field
left test field