Nvis 5586A
Nvis Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
37
Hardware Description
CPU:
8086 is a 16 bit, third generation microprocessor and is suitable for an exceptionally wide
spectrum of microcomputer applications. This flexibility is one of most outstanding
characteristics.
8086 has got 16 data lines and 20 address lines. The lower 16 address lines are multiplexed
with 16 data lines. Hence it becomes necessary to latch the address lines. This is done by
using 74 LS 373. In fact several of the 40 CPU pins have dual functions that are selected by
a strapping pin. In this kit 8086 is used in the max. mode (MN/MX input held logically low).
The 8088 is designed with an 8-bit external path to memory and I/O. Except that the 8086
can transfer 16 bits at a time, the two processors & software are identical in almost every
respect. Software identical in almost every respect. Software written for one CPU will
execute on the other without alteration. The two processors are designed to operate with the
8089 I/O processors and other processors in multiprocessing and distributed processing
systems.
The INTR, TEST & Hold Inputs to 8086 are pulled down and are brought out at PCB FRC
connector.
The mask able interrupt INTR is available to the peripheral circuits through the expansion
Bus. To use the mask able interrupt an interrupt vector pointer must be provided on the data
bus when INTA is active. An interrupt Controller Circuit is provided to take care of more
than one source of interrupt.
Co-Processor 8087:
The 8087 Co-processor ―hooks‖ have been designed into the 8086 and 8088 so that these
types of processor can be accommodated in the future. A co-processor differs from an
independent processor in that it obtains its instructions from another processor, called a host.
The co-processor monitors instructions fetched by the host and recognizes certain of these as
its own and executes them. A co-processor, in effect, extends the instruction set of its host
computer.
I/O Processor 8089:
The 8086 and 8088 are designed to be used with the 8089 in high performance I/O
applications. The 8089 in conceptually resembles a microprocessor with two DMA channels
and an instruction set specifically tailored for I/O operations. Unlike simple DMA
controllers, the 8089 can service I/O devices directly, removing this task from the CPU. In
addition, it can transfer data on its own bus or on the system bus, can match 8-bit or 16-bit
peripherals to 8-bit or 16-bit buses, and can transfer data from memory to memory and from
I/O devices to I/O device. 8089 has been used here in local mode. The system bus, can
match 8-bit or 16-bit peripherals to 8-bit or 16-bit buses, and can transfer data from memory
to memory and from I/O devices to I/O device. 8089 has been used here in local mode.
Clock Generation:
Summary of Contents for 5586A
Page 2: ...Nvis 5586A Nvis Technologies Pvt Ltd 2...
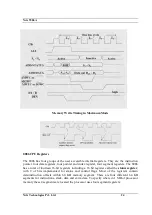
Page 23: ...Nvis 5586A Nvis Technologies Pvt Ltd 23 Memory Read Timing in Maximum Mode...
Page 30: ...Nvis 5586A Nvis Technologies Pvt Ltd 30...
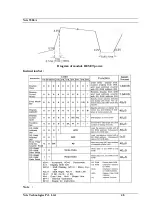
Page 48: ...Nvis 5586A Nvis Technologies Pvt Ltd 48 Diagram of module RESET power Instruction Set Note...