34
Chapter 3 CS 1000 considerations
N0060720
N0060720
Cross-reference for CS 1000 and SRG50 terminology
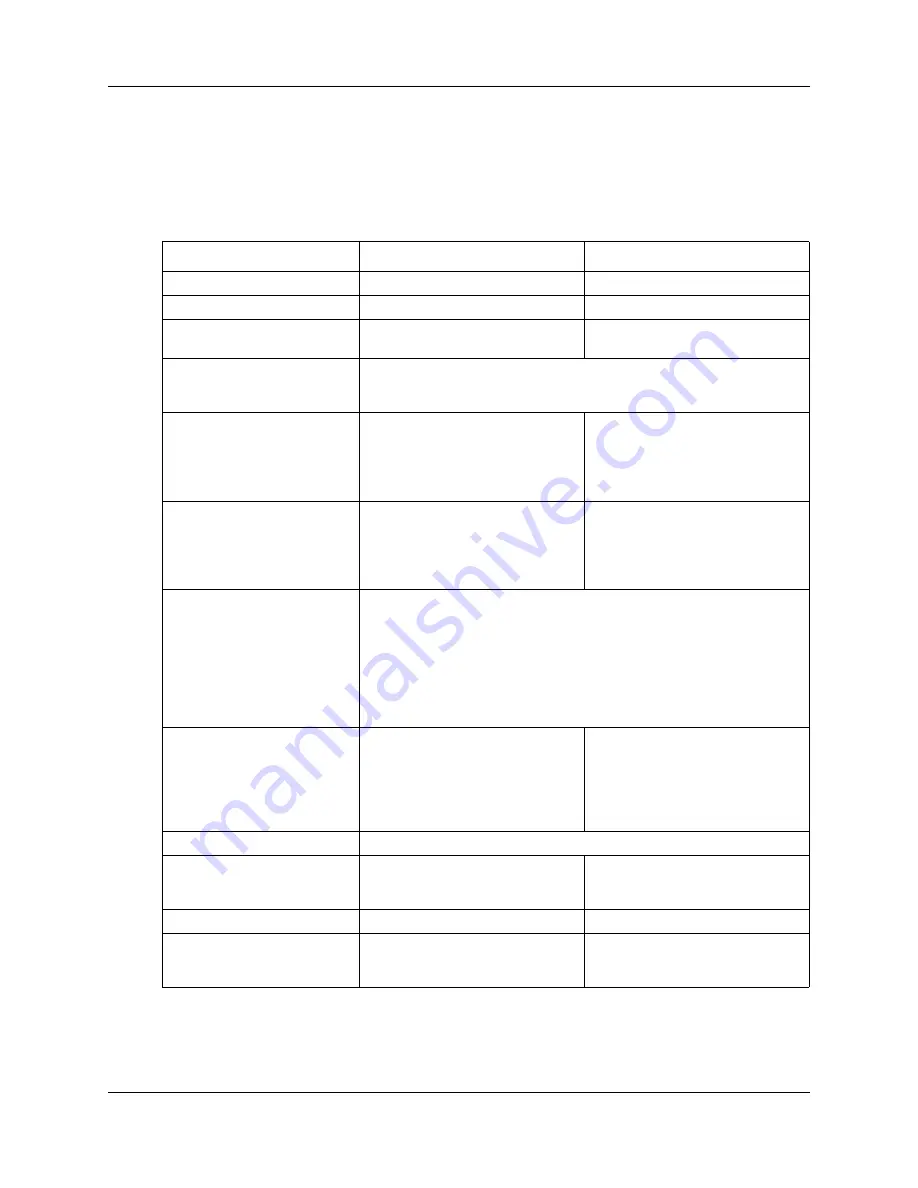
The following table compares configuration-related terms and contexts of the CS 1000 and the
SRG50.
Table 2
Comparison of CS 1000 and SRG50 terms and contexts (Sheet 1 of 2)
Term or Context
CS 1000
SRG50
Dialing plan
on-net / off-net dialing
Private / Public network dialing
Type of number
CDP / UDP / GDP / TNDN
CDP / UDP / no equivalent
Numbers
TN (terminal number)
MOTN (main office terminal
number)
TN = MOTN. That is, the TN from the main office is entered on the SRG50
in the MOTN field (refer to
“Configuring IP telephones for redirection” on
page 46
).
BUID (branch user ID)
The dialable number of an IP
telephone at the SRG50 when it is
called from a phone located at the
main office or another branch office.
The CS 1000 BUID is entered on
the SRG50 (refer to
“Datafilling the
S1000 IP Terminal Details panel” on
page 48
) but there is no SRG50
equivalent for BUID.
DN (directory number)
The dialable number of a telephone
at the main office when it is called
from another phone at the main
office.
DN (directory number)
The dialable number of a telephone
at the SRG50 when it is called from
another phone at the SRG50.
In the case of a CDP dialing plan, it is recommended that the BUID and
the SRG50 DN be the same.
In the case of a UDP dialing plan, the BUID has the form: <VOIP Trunk
Access Code> + <LOC> + <DN>. In this case, it is recommended that the
SRG50 DN be the same as <DN>.
The dialable number of an IP telephone at the SRG50, when dialed from
another phone at the SRG50, remains the same in both normal and local
mode if the preceding recommendations are implemented.
AC1
VOIP Trunk Access Code (refer to
“CS 1000 information for the
SRG50” on page 43
)
Destination code for VoIP trunks
(refer to
“Call routing: configuring for
outgoing calls” on page 86
)
AC1 = VOIP Trunk Access Code = Destination code for VoIP trunks
Routing
distant steering codes (DSC), trunk
steering codes (TSC), local steering
codes (LSC)
call routing, destination codes, line
pool access codes
digit manipulation table
dialout digits (routing)
Numbering Plan ID
ISDN/Telephony (E.164), Private,
Telephony (E.163), Telex (F.69),
Data (X.121), National Standard
Private
Summary of Contents for SRG50
Page 1: ...Part No N0060720 03 December 2007 Survivable Remote Gateway 50 Configuration Guide...
Page 4: ...4 Task List N0060720 N0060720 Glossary 107 Index 109...
Page 8: ...8 Contents N0060720...
Page 26: ...26 Chapter 1 Getting started N0060720 N0060720...
Page 50: ...50 Chapter 3 CS 1000 considerations N0060720 N0060720 Figure 6 S1000 IP Terminal Details panel...
Page 62: ...62 Chapter 4 CS 2000 considerations N0060720 N0060720...
Page 100: ...100 Chapter 8 Troubleshooting N0060720...
Page 106: ...106 Telephone features in normal and local mode N0060720...
















































