Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
UD-series Screw Compressors
6-9
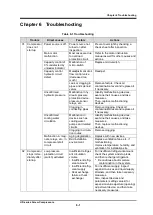
Trouble
Direct causes
Factors
Actions
11
Abnormal
vibration
and/or
noise of
compressor
Oil hammer
Continuous low
load operation at
below 30 % of
capacity control
During low load operation, lubricant
is poorly discharged. Because of
this, the amount of oil that remains
inside rotor mesh increases and oil
becomes compressed.
→
Avoid continuous low load opera-
tion.
* Especially for light gas such as
He and NH3, 10 minutes low load
operation has a negative effect.
For fluorocarbons, low load
operations of more than 30
minutes are not recommended
Liquid flow-back
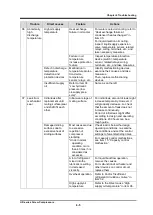
during startup
* Initial abnormal
noises are
conspicuous.
→If this
phenomenon
happens, in some
cases,
compressor gets
instantly
damaged.
When compressor
is stopped,
refrigerant is
liquefied and
remains in
upstream piping.
This is due to various factors such
as a leak inside the liquid supply
solenoid valve on load side,
insufficient heat exchange
(refrigerant evaporation) in heat
exchanger, or liquid trapping
caused by wrong piping in piping
route.
→Identify the causes (more than
one may exist), and take
measures. Then, perform an
overhaul of the compressor.
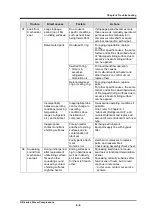
Liquid flow-back
during operation
* Frosting on
suction side is
conspicuous.
* In many cases,
the phenomenon
is often
“mist-back”
(suction of moist
steam) rather
than liquid
flow-back.
* To prevent this
phenomenon,
gas
‐
liquid
separator
(accumulator)
can be installed.
* Refer to Factor
“Insufficient
refrigerant
circulation
volume” in item
02 as well.
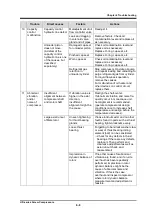
Opening for liquid
supply expansion
valve is too large.
For temperature type expansion
valve, inspect temperature sensitive
cylinder and capillary tube.
Take measures if any defects are
found.
For incompatible orifice due to the
change in operating conditions,
replace orifice.
For electronic expansion valve,
inspect devices on expansion valve
opening control devices (circuit)
such as temperature sensor,
converter, controller (over-heating
regulator). If any defects are found,
replace the faulty devices.
As with temperature type expansion
valve, for incompatible orifice due to
the change in operating conditions,
replace orifice.
Rapid change from
unloaded operation
to full load
operation
Set control parameters so that rapid
change will not occur.
Or, re-adjust opening of oil
controller valve on capacity control
increase side towards the decrease
side.