Page 509
T31 SERIES
5.
Figure 5-1
PUMP ENDS
A.
Preliminary
B.
Disassembly
C.
Inspection of Components
D.
Reassembly
E.
Testing and Final Adjustments
5A Preliminary
Before attempting any service on the
pump or motor, disconnect the electri-
cal power to the pump motor. If the
pump and motor are to be removed as
a unit, note the wiring confi guration.
Use colored or numbered tape to mark
the wire connections of the motor and
power source, for reconnection. If the
pump is being used to pump hot liquid,
let the pump and liquid cool before
starting disassembly.
1. Disconnect the inlet and outlet pip-
ing before unbolting the pump and
motor. If the pipes are corroded,
use penetrating oil on the threads to
aid in removal.
2. Unbolt the motor from the base and
remove the unit. All work on the unit
should be performed on an elevated
workbench whenever possible.
5B Disassembly
The following tools and equipment are
needed for disassembly of T31 Series
Pumps:
1. Soft plastic or wooden mallet.
2. Small ball peen hammer.
3. 10mm wrench or socket
4. Snap ring pliers.
5. Penetrating oil.
6. 11/16" wood dowel (Approx. 6"
long.)
7. Thin blade screwdriver.
8. Cealube G or similar glycol base
lubricant. (DO NOT use petroleum
products.)
To disassemble the pump:
Refer to Figure 5-2 for reference to
the numbered parts in the procedures
below.
1. Remove all liquid from the pump.
Air blown through the pump will
remove the water quickly.
2. Remove the four (4) M6-1 X 80mm
bolts (#19) from the cover (#2).
3. Remove the cover. In some cases
light tapping with a plastic or wooden
mallet on the outside diameter of the
cover may be required to loosen it
from the motor bracket. Care should
be taken if a screwdriver is needed
to pry between the cover and motor
bracket. Damage to the “O” ring
(#7) and/or impeller (#11) can result.
4. Remove the impeller. This is easily
done by setting the motor on end.
The impeller is a slip fi t and under
normal conditions, can be removed
by hand or by gently tapping on the
end of the shaft with a mallet. Strik-
ing the shaft too hard could damage
the seat, rotating element, or the
motor. After removing the impeller,
the impeller key (#23) needs to be
removed from the shaft keyway.
5. Remove the snap ring (#4) from the
shaft; note the spring that is held in
place by the snap ring. Remove the
spring from the shaft.
6. To remove the rotating element
(#12), gently slide the motor bracket
(#1) forward on the shaft to move
the rotating element high enough
to be removed by hand. Using
tools on the rotating element may
damage the rotating element or the
seat. Take precautions to keep the
rotating element clean if it is to be
reused.
7. Next remove the motor bracket.
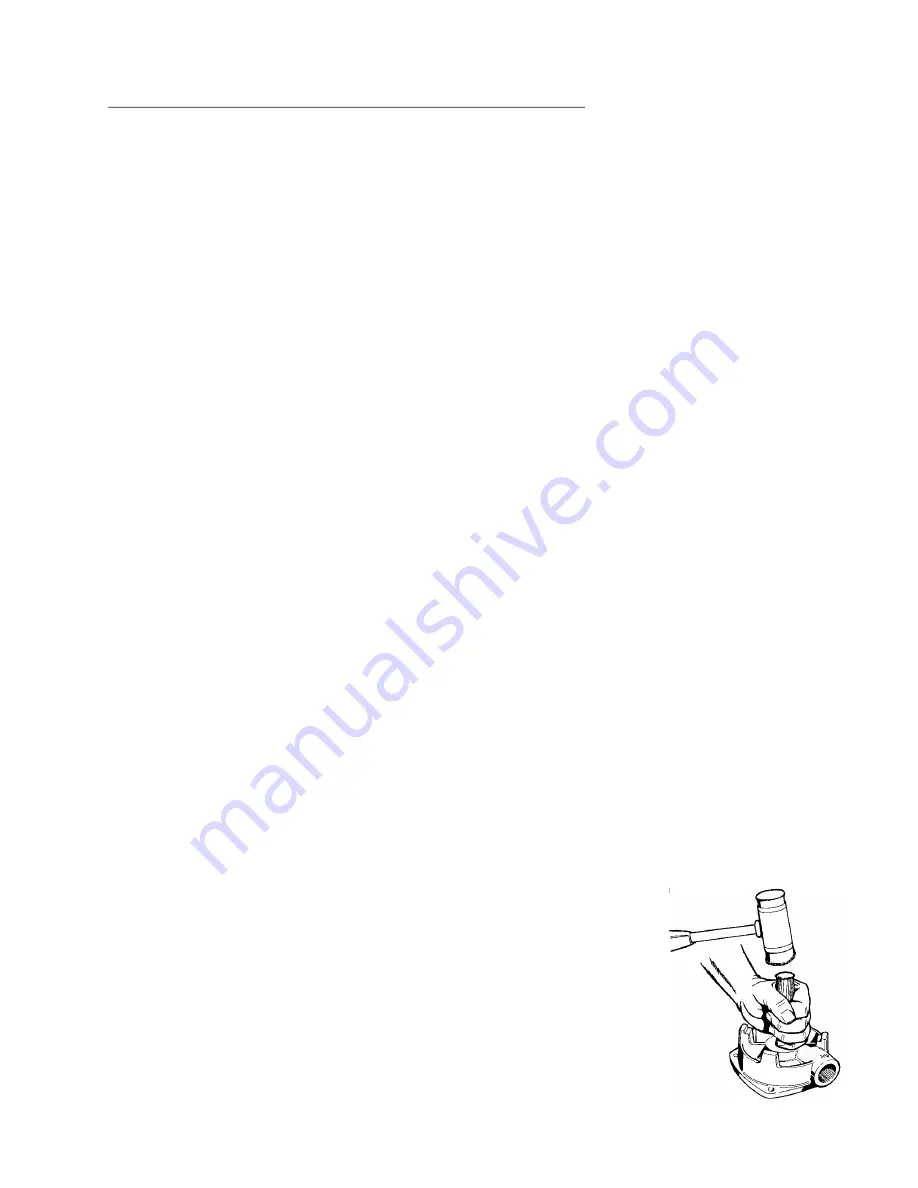
8. To remove the seat (#125). Refer to
Figure 5-1. Place the motor bracket
face down on a clean fl at surface.
Look into the opening in the center
of the motor bracket, and you will
see a portion of the seat. Insert the
11/16" dowel and, very gently, tap
the seat until it drops out. Care
must be taken with the seat. It is
often a brittle material and is prone
to breakage.
It is recommended
that a new replacement seat be
installed during reassembly.
5C Inspection of Components
Thoroughly clean all parts. All compo-
nents should be examined for wear and
corrosion. Replace any parts that show
visible wear. If the pump was not pro-
ducing suffi cient pressure or capacity,
the clearances between the rings and
impeller probably exceed the maximum
allowable clearance. At minimum the
impeller should be replaced in this
case. If the total side running clear-
ance for an impeller exceeds .007", it
is unlikely that pump performance will
reach that of a new pump except at
lower discharge pressures.
The “O” rings and other elastomeric
components should be replaced if they
have been deformed or cut.
If seal components must be reused,
carefully inspect for microscopic cracks
and nicks. Scratches that might be ig-
nored elsewhere can produce leakage
if they are on seal carbons and seat
wearing surfaces.
Cleanliness is imperative when working
with mechanical seals. Almost un-
noticeable particles between seal faces
can be, and often are, the cause of
early seal failures.
Check the impeller; it is designed to
fl oat. It should move easily on the
shaft. As long as it can be moved on
the shaft by hand, it is loose enough. If
the impeller can be rocked or wobbled,
it is too loose and must be replaced.
Check the shaft for galling, pitting,
and corrosion. If the shaft is corroded
where the seal comes in contact with
the shaft, the motor or bearing pedestal
shaft must be replaced. Surface cor-
rosion must be removed so that seals
can slide freely during assembly. The
shaft diameter should be no smaller
than .002" below the nominal fractional
seal sizes. Remove any nicks or burrs
which may have occurred during disas-
sembly. Reclean parts as necessary.
5D Reassembly
All parts should be visually inspected
and cleaned or replaced as outlined in
5C above.
Service


































