Section 2 - On the Water
Page 14
90-8M0093150
eng
MAY 2014
Exhaust Emissions
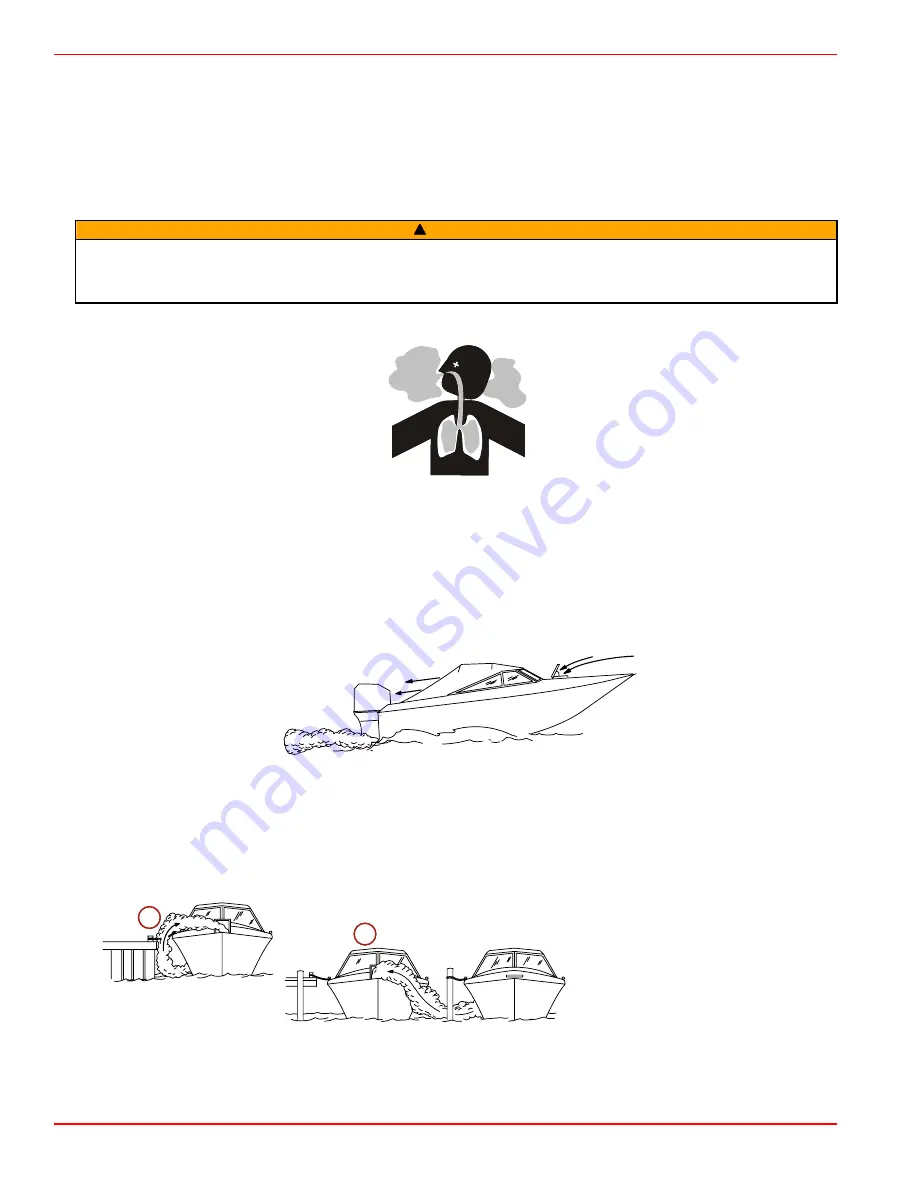
Be Alert to Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a deadly gas that is present in the exhaust fumes of all internal combustion engines, including the
engines that propel boats, and the generators that power boat accessories. By itself, CO is odorless, colorless, and tasteless,
but if you can smell or taste engine exhaust, you are inhaling CO.
Early symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning, which are similar to the symptoms of seasickness and intoxication, include
headache, dizziness, drowsiness, and nausea.
!
WARNING
Inhaling engine exhaust gases can result in carbon monoxide poisoning, which can lead to unconsciousness, brain damage,
or death. Avoid exposure to carbon monoxide.
Stay clear from exhaust areas when engine is running. Keep the boat well‑ventilated while at rest or underway.
Stay Clear of Exhaust Areas
41127
Engine exhaust gases contain harmful carbon monoxide. Avoid areas of concentrated engine exhaust gases. When engines
are running, keep swimmers away from the boat, and do not sit, lie, or stand on swim platforms or boarding ladders. While
underway, do not allow passengers to be positioned immediately behind the boat (platform dragging, teak/body surfing). This
dangerous practice not only places a person in an area of high engine exhaust concentration, but also subjects them to the
possibility of injury from the boat propeller.
Good Ventilation
Ventilate the passenger area, open side curtains or forward hatches to remove fumes.
Example of desired air flow through the boat:
21622
Poor Ventilation
Under certain running and/or wind conditions, permanently enclosed or canvas enclosed cabins or cockpits with insufficient
ventilation may draw in carbon monoxide. Install one or more carbon monoxide detectors in your boat.
Although the occurrence is rare, on a very calm day, swimmers and passengers in an open area of a stationary boat that
contains, or is near, a running engine may be exposed to a hazardous level of carbon monoxide.
1. Examples of poor ventilation while the boat is stationary:
a -
Operating the engine when the boat
is moored in a confined space
b -
Mooring close to another boat that
has its engine operating
21626
a
b