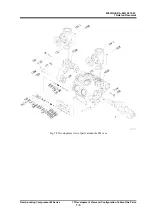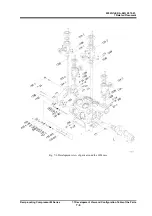
2202G1JE-DA-M-N_2010.01.
6
Troubleshooting
Reciprocating Compressor M Series
6.1
Troubleshooting
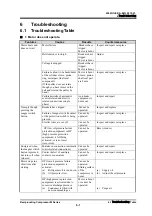
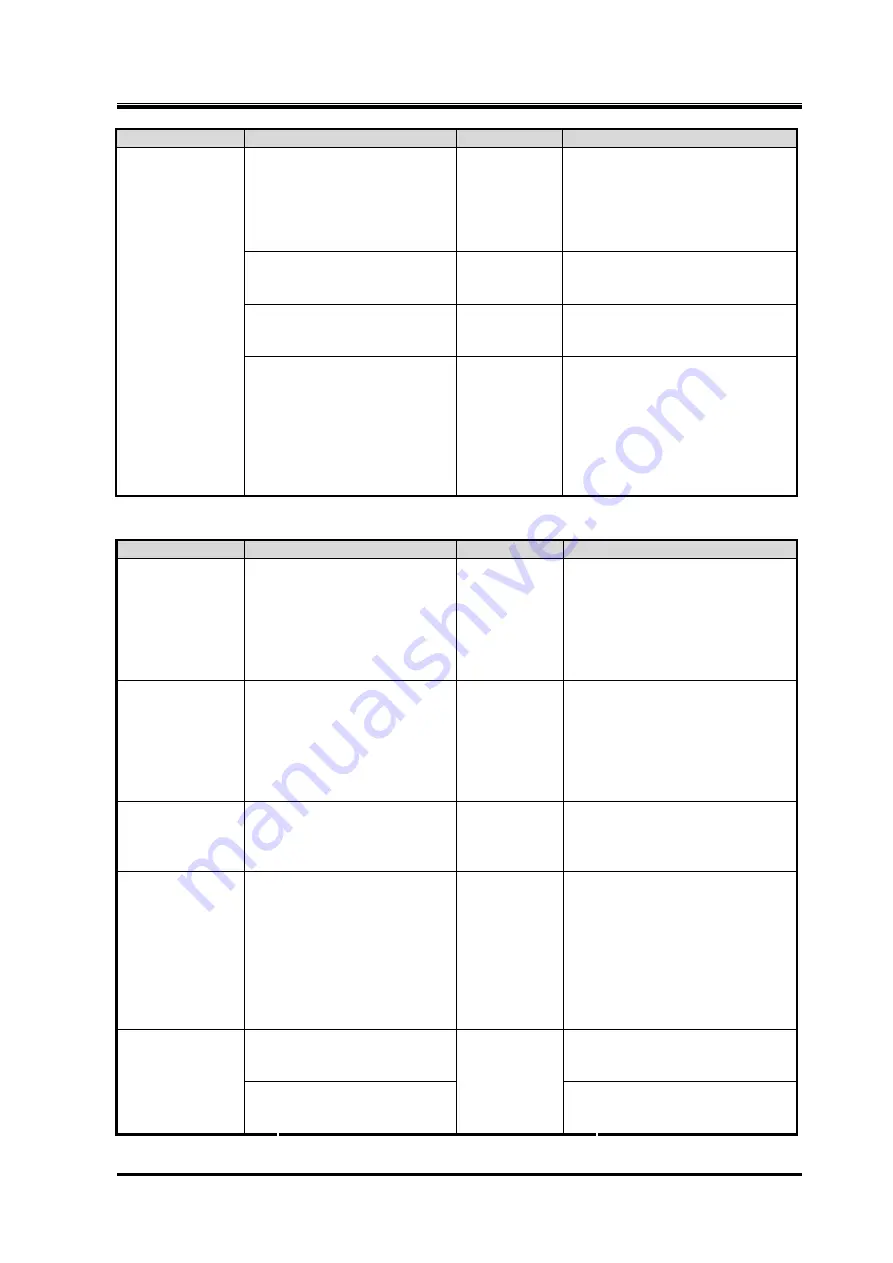
Table
6-2
Features
Causes
Results
Countermeasures
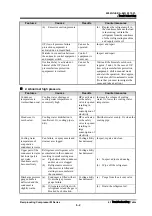
(b) Excessive suction pressure
(b)
Replace the refrigerant oil in
the crankcase because the load
is increasing, or drain the
refrigerant from the crankcase
of other refrigerating machine
and supply warm oil.
OP (low oil pressure failure
protection equipment) is
activated due to liquid back.
Cannot be
operated
Inspect and repair
Mistake in connection between
the automatic control equipment
and magnet switch
Control
equipment is
burnt out.
Inspect and repair
Overload relay is activated or
bimetal of the OP (low oil
pressure failure protection
equipment) is warmed.
Cannot be
started
Wait until the bimetal cools down
(approx. 5 min.). In the case of OP
(low oil pressure failure protection
equipment), shift to manual mode
and start the operation. After approx.
10 minutes, shift to automatic mode.
(Note that you must investigate the
cause and take an action.)
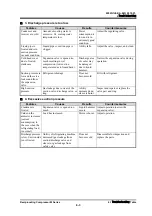
2. Abnormal high pressure
Features
Causes
Results
Countermeasures
Condenser
temperature is
warmer than usual.
Cooling water shortage or
cooling water temperature is
excessively high.
HP is activated
or the safety
valve is opened
resulting in
large
consumption of
electricity.
Increase the volume of cooling
water. Or, lower the cooling water
temperature.
Head cover is
overheated.
Cooling water distribution is
insufficient. Or, cooling pipe is
dirty.
HP is activated
or the safety
valve is opened
resulting in
large
consumption of
electricity.
Distribute water evenly. Or, clean the
cooling pipe.
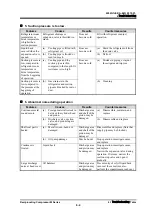
Cooling water
temperature of
evaporative
condenser is warm.
Fan failure, or spray nozzle and
strainer are clogged.
Cooling ability
has decreased.
Inspect, repair, and clean
Refrigerant or refrigerant oil is
accumulated in the condenser
resulting in small cooling area.
(a)
Pipe between the condenser
and receiver is clogged.
(a)
Inspect, adjust, and unclog
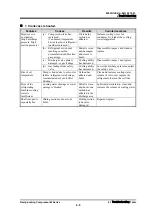
Upper part of the
condenser is warm
but lower part is
not warm.
Crankcase easily
becomes frosty.
(b) Refrigerant is excessive
(the receiver is filled and
starting to accumulate in
the condenser).
Cooling ability
has decreased.
(b)
Wipe off the refrigerant.
(a)
Condenser is filled with air.
Or, discharge pressure
gauge failure
(a)
Purge from the air vent valve.
Discharge pressure
gauge needle is
deflected and the
condenser is
slightly warm.
(b) Oil separator is filled with
refrigerant oil and the gas is
blocked by obstruction.
Cooling ability
has decreased.
(b)
Drain the refrigerant oil.