A-11
INSTALLATION
VANTAGE
®
520 SD
CABLE INDUCTANCE AND ITS EFFECTS ON
WELDING
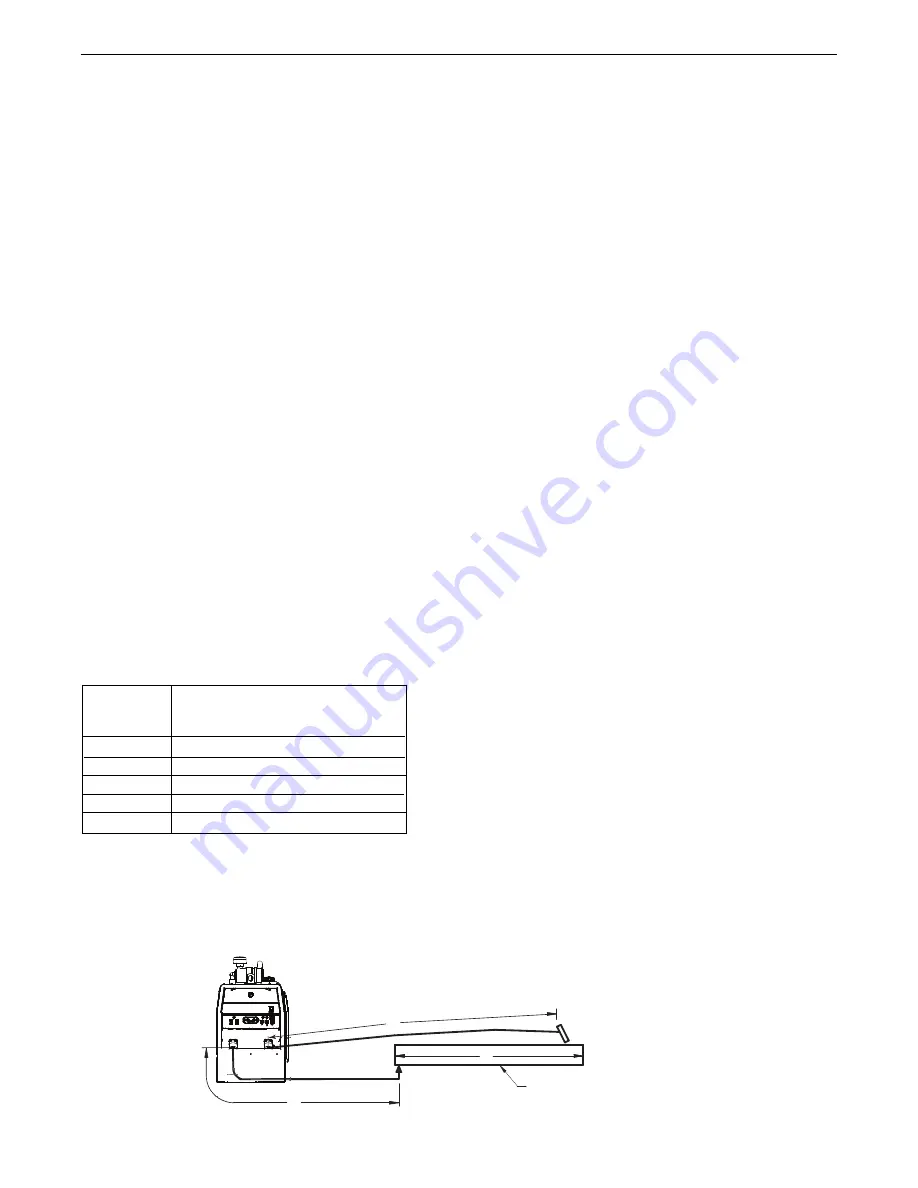
Excessive cable inductance will cause the welding performance to
degrade. There are several factors that contribute to the overall
inductance of the cabling system including cable size, and loop
area. The loop area is defined by the separation distance between
the electrode and work cables, and the overall welding loop
length. The welding loop length is defined as the total of length of
the electrode cable (A) + work cable (B) + work path (C) (See
Figure A.9).
To minimize inductance always use the appropriate size cables,
and whenever possible, run the electrode and work cables in close
proximity to one another to minimize the loop area. Since the most
significant factor in cable inductance is the welding loop length,
avoid excessive lengths and do not coil excess cable. For long
work piece lengths, a sliding ground should be considered to keep
the total welding loop length as short as possible.
Electrode Voltage Sensing
The remote ELECTRODE sense lead (67) is built into the 5-pin
ArcLink control cable and is always connected to the wire drive
feed plate when an ArcLink wire feeder is present. Enabling or
disabling electrode voltage sensing is application specific, and
automatically configured by the active weld mode.
Voltage sense leads requirements are based on the weld process
(See Table A.3).
CONTROL CABLE CONNECTIONS
General Guidelines
Genuine Lincoln control cables should be used at all times (except
where noted otherwise). Lincoln cables are specifically designed
for the communication and power needs of the
Engine Welder and
Power Feed
™
systems. Most are designed to be connected end to
end for ease of extension. Generally, it is recommended that the
total length not exceed 200ft. (60.960m). The use of non-standard
cables, especially in lengths greater than 25 feet, can lead to
communication problems (system shutdowns), poor motor accel-
eration (poor arc starting), and low wire driving force (wire feeding
problems). Always use the shortest length of control cable possi-
ble, and
DO NOT coil excess cable.
Regarding cable placement, best results will be obtained when
control cables are routed separate from the weld cables. This min-
imizes the possibility of interference between the high currents
flowing through the weld cables, and the low level signals in the
control cables.
Product specific Installation Instructions
Connection Between VANTAGE
®
520 SD and ArcLink
®
Compatible
Wire feeders (K1543, K2683 – ArcLink
®
Control Cable)
The 5-pin ArcLink
®
control cable connects the VANTAGE
®
520 SD
to the wire feeder. The control cable consists of two power leads,
one twisted pair for digital communication, and one lead for voltage
sensing. The 5-pin ArcLink
®
connection on the VANTAGE
®
520 SD
is located on control panel. The control cable is keyed and polar-
ized to prevent improper connection. Best results will be obtained
when control cables are routed separate from the weld cables,
especially in long distance applications. The recommended com-
bined length of the ArcLink
®
control cable network should not
exceed 200ft. (60.960m).
FIGURE A.9
B
A
C
WORK
VANTAGE
520 SD
Process
GMAW
GMAW-P
FCAW
GTAW
SMAW
Electrode Voltage Sensing
(1)
67 lead
67 lead
67 lead
67 lead
Voltage sense at studs
Voltage sense at studs
TABLE A.3
(1)
The electrode voltage sense lead (67) is automatically
enabled by the weld process, and integral to the 5 pin
ArcLink control cable
(K1543-xx) or K2683-xx.
Summary of Contents for VANTAGE 520 SD
Page 8: ...8 NOTES VANTAGE 520 SD ...
Page 20: ...A 12 NOTES VANTAGE 520 SD ...
Page 49: ...F 3 CONNECTION DIAGRAMS VANTAGE 520 SD ...
Page 50: ...F 4 CONNECTION DIAGRAMS VANTAGE 520 SD ...
Page 51: ...F 5 CONNECTION DIAGRAMS VANTAGE 520 SD ...
Page 56: ...F 10 NOTES VANTAGE 520 SD ...
















































