Model KVVB Instructions
Page 3 of 5
Any meter or non-potentiometric measurement system will load the output of the KVVB,
affecting its ratio accuracy. To limit the error due to meter loading to less than 0.01 %, the meter
impedance should be greater than 10 G
For best accuracy, the loading effect on the KVVB can be
calculated, and a correction can be applied to the measured result. To determine this correction, apply
the below equation (1/X = 1/A + 1/B):
1 / (result) =
1 / (KVVB output impedance) + 1 / (meter input impedance)
Example: (KVVB output 50 K
; meter input impedance 10 M
):
1 / (result) =
1 / (10,000,000) + 1 / (50,000) = 0.000 020 1
Result
=
1/0.000 020 1 = 49,751.24 ohms (= loaded output impedance of KVVB)
The 1,000:1 ratio is based on a resistance ratio of 50 M
(total) to 50 K
(output). If the loaded
output resistance is 49,751.24 ohms, the actual ratio will be:
50,000,000 / 49,751.24 = 1,005.00 : 1
Measuring 10,000 volts in this example will read on the meter as 9.950 25 volt, or 1/1,005 of the
actual voltage. If using a voltmeter, insure that the input impedance is set to >10 G ohm to minimize
loading errors.
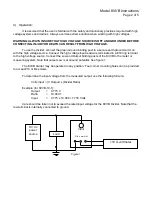
5) Calibration:
Either of two calibration methods may be used. One is comparison against a calibrated high
voltage divider; the other is calibration using a high voltage Wheatstone bridge circuit.
For comparison calibration:
1) Connect the KVVB and a calibrated standard high voltage divider (such as Ohm-Labs HVS) to a
secure ground using ground cables of equal length and gauge.
2) Connect two calibrated voltmeters to the outputs of the standard and the KVVB.
3) Connect the high voltage source to the standard and to the KVVB inputs.
4) Apply a low setting of the high voltage supply to verify operation.
5) Apply high voltage to both units. Allow applied voltage to settle for 15 minutes to allow full
stabilization of the KVVB. Use the ratio of the calibrated standard and the meter readings to
determine the KVVB ratio.
(Standard Divider Output Voltage x Standard Divider Ratio) / KVVB voltage = Ratio