CV-M9 GE
- 18 -
Manual white balance
By adjusting the Red (Register 0xA0C8); Blue (Register 0xA0CC) and Master Gain (Register
0xA0C4) gains settings, it is possible to achieve a proper white balance output from the camera
for a wide range of color temperatures. The recommended method is to point the camera at a
white target, and adjust gain settings until image on the screen matches the target.
One-push white balance
.
(Set register 0xA0D0 to 0x00)
If this register is set, an automatic white balance is performed once. To use this function the
camera must be operating in the continuous mode.
The result of this function (0 = complete; 1 = too dark; 2 = too bright; 3 = timeout; 4 = busy; 5 =
out of range; 6 = trigger mode not set to continuous) can be read out of register 0xA0D8.
Please see the register map for complete details of the register settings and responses.
lower right
lower middle
lower left
middle right
middle
middle left
upper right
upper middle
upper left
lower right
lower middle
lower left
middle right
middle
middle left
upper right
upper middle
upper left
Full
Full
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
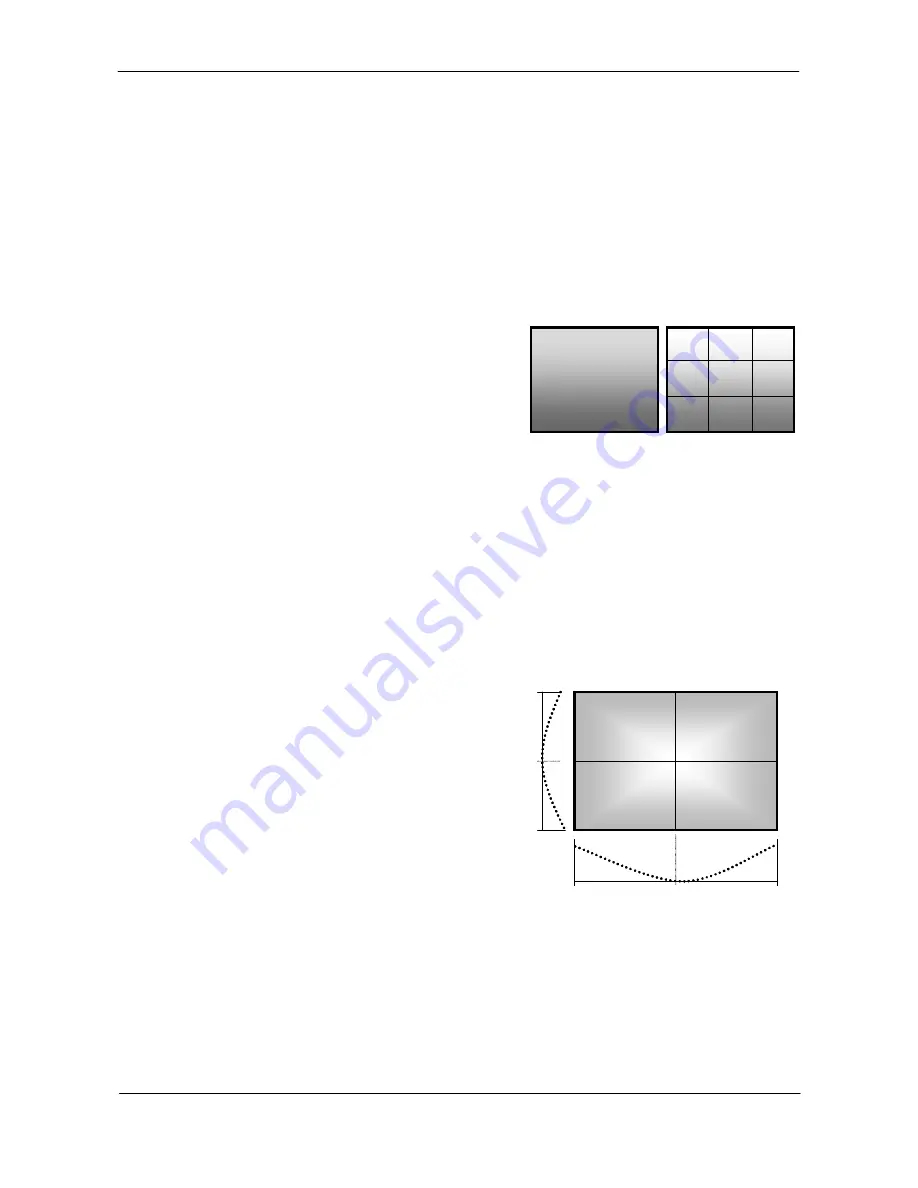
S
et Auto White Balance area
.
With this function it is possible to select which part of
the image the automatic white balance function uses to
calculate the gain settings.
The register 0xA0D4 is used to set this function.
Fig. 10. Auto white balance areas.
8.3.2. White balance (by individual R, G and B channel shutter settings)
In order to achieve proper white balance without compromising signal-to-noise ratio, it is
possible to adjust the exposure (shutter) time of each R, G and B channel individually. Please
see chapter 8.3.6. Electronic Shutter for details on how to set this function.
8.3.3. Automatic Dynamic shading correction
The CV-M9GE camera has a digital shading correction circuit, which can compensate for prism
chromatic shading, for lens shading and for CCD shading. It makes the choice of lenses wider.
The camera with a given lens and a given f-number is looking on a homogeneous white scene.
A horizontal profile of the shading in 128 points is made for the 3 colors.
A vertical profile of the shading in 96 points is
made for the 3 colors. The average level of each
divisions for R,G and B respectively is compared
with the level of the image centre and the level
difference compensates the video data. The
resulting image is then compensated for shading
caused by the lens, prism and CCD.
0
127
0
95
H shading data
V
shading
data
0
127
0
95
H shading data
V
shading
data
Fig. 11. Dynamic shading correction.
The factory setting is done with a Fujinon 15mm F2.2 lens, with the iris is set to F5.6.
Note: Lens requirements
.
Although the shading correction widens the choice of lenses for this camera, it is recommended
to use lenses designed for 1/3” 3 CCD cameras to obtain the best image quality. As chromatic
shading depends of the focal length and the iris setting of the lens, avoid using wide-angle
lenses, and working with the lens iris setting fully open.






























