23
441 01 5003 01
Specifications are subject to change without notice
3.
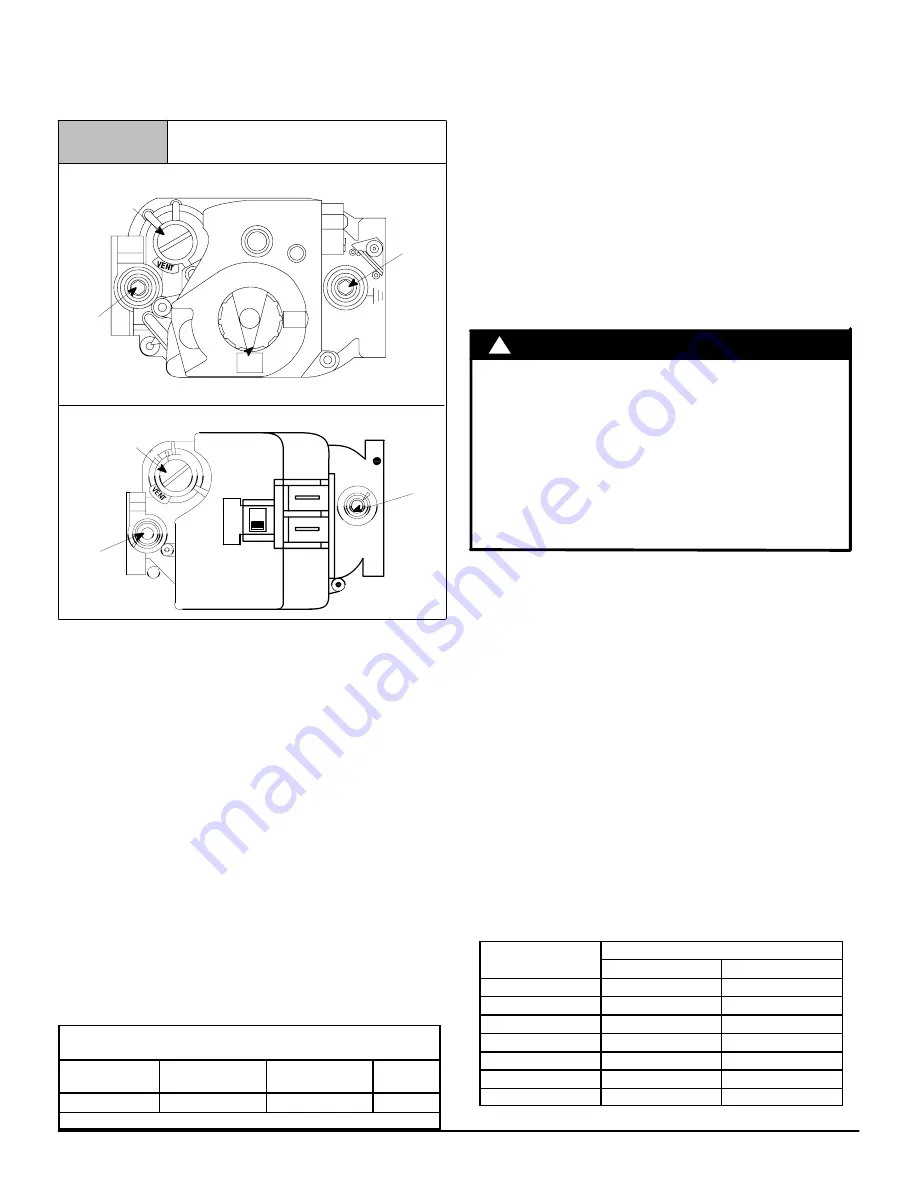
Remove
manifold pressure adjustment screw cover on
furnace gas valve. Turn adjusting screw counterclockwise to
decrease manifold pressure and clockwise to increase
pressure.
Typical Gas Valve Honeywell
Figure 27
V
T
25--24--98a
HONEYWELL
ON
OFF
Regulator Adjustment
Under Cap
Inlet
Pressure
Tap
1
/
8
NPT
INLET
OUTLET
Outlet
Pressure
Tap
1
/
8
NPT
Regulator Adjustment
Under Cap
Inlet
Pressure
Tap
1
/
8
NPT
INLET
OUTLET
Outlet
Pressure
Tap
1
/
8
NPT
IN
OFF
ON
H
O
N
EYW
ELL
NOTE:
Adjustment screw cover
MUST
be replaced on gas valve
before reading manifold pressure and operating furnace.
4. Set manifold pressure to value shown in
Table 7
or
Table 8
.
5. When the manifold pressure is properly set, replace the
adjustment screw cover on the gas valve.
6. Remove jumper wire from thermostat connection on control
board.
Remove manometer connection from manifold
pressure tap, and replace plug in manifold.
7. Check for leaks at plug.
Natural Gas Input Rating Check
The gas meter can be used to measure input to furnace.
Check with gas supplier for actual BTU content.
1. Turn
OFF
gas supply to all appliances other than furnace and
start furnace. Use jumper wire on R to W.
2. Time how many seconds it takes the smallest dial on the gas
meter to make one complete revolution.
Note:
If meter uses a 2 cubic foot dial, divide results (seconds) by
two.
Refer to
Example.
The Example is based on a natural gas BTU
content of 1,000 BTU’s per cubic foot.
Example
Natural Gas
BTU Content
No. of Seconds
Per Hour
Time Per Cubic
Foot in Seconds
BTU Per
Hour
1,000
3,600
48
75,000
1,000 x 3,600
÷
48 = 75,000 BTUH
3. Remove jumper wire from R to W.
4. Relight all appliances.
Orifice Sizing
NOTE:
Factory sized orifices for natural and Propane gas are listed
in the furnace Technical Support Manual.
Ensure furnace is equipped with the correct main burner orifices.
Refer to
Table 5
,
Table 6
,
Table 7
or
Table 8
for correct orifice size
and manifold pressure for a given heating value and specific gravity
for natural and propane gas.
Operation Above 2000
′
Altitude
FIRE,
EXPLOSION,
CARBON
MONOXIDE
POISONING HAZARD.
Failure to follow these instructions exactly could
result in personal injury, death and/or property dam-
age.
This high--altitude gas--conversion shall be done by
a qualified service agency in accordance with the
Manufacturer’s instructions and all applicable
codes and requirements, or in the absence of local
codes, the applicable national codes.
!
WARNING
These furnace may be used at full input rating when installed at
altitudes up to 2000
′
. When installed above 2000
′
, the input must be
decreased 2% (natural) or 4% (Propane) for each 1000
′
above sea
level. This may be accomplished by a simple adjustment of
manifold pressure or an orifice change, or a combination of a
pressure adjustment and an orifice change. The changes required
depend on the installation altitude and the heating value of the fuel.
Table 5
&
Table 6
or
Table 7
&
Table 8
show the proper furnace
manifold pressure and gas orifice size to achieve proper
performance based on elevation above sea level for both natural
gas and propane gas.
To use the natural gas table, first consult your local gas utility for the
heating value of the gas supply. Select the heating value in the first
column and follow across the table until the appropriate elevation
for the installation is reached. The value in the box at the
intersection of the altitude and heating value provides not only the
manifold pressure but also the orifice size. In the natural gas tables
the factory--shipped orifice size is in bold (
42
). Other sizes must be
obtained from service parts.
High Altitude Input Rate =
Nameplate Sea Level Input Rate x (Multiplier)
Elevation
High Altitude Multiplier
Natural Gas
Propane Gas
0 - 2000
′
1.00
1.00
2001
′
- 3000
′
0.95
0.90
3001
′
- 4000
′
0.93
0.86
4001
′
- 5000
′
0.91
0.82
5001
′
- 6000
′
0.89
0.78
6001
′
- 7000
′
0.87
0.74
7001
′
- 8000
′
0.85
0.70
*
Based on mid--range of elevation.
















































