rate (see the hpssgui/hpssadm man pages for more details).
If a server is configured as executable but is not running, SSM will treat it as an error.
Therefore, if a server is not intended to run for an extended period, its Executable flag should be
unchecked. SSM will stop monitoring the server and will not report the server-not-running
condition as a critical error. This will also help reduce the work load for SSM.
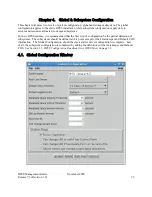
Type
. Indicates the type of the server in acronym form. Possible values include CORE, GK,
LOGC, LOGD, LS, MPS, MOVER, PVL, various PVR values, SSMSM, and SUD. See the
glossary for the meanings of these acronyms.
Subtype.
Indicates the subtype of the server, sometimes in acronym form. Not all servers have
subtypes. Possible values (particularly PVR subtypes) include SCSI, STK, 3494, Operator,
AML, and 3584 LTO. See the glossary for the meanings of these acronyms.
Subsystem
. The name of the storage subsystem to which the server is assigned. Only servers of
type Core and MPS should have a subsystem name. For all other server types this column should
be blank.
Op State
. The operational state of the server as reported by the server itself:
•
Enabled - The server is operating normally.
•
Disabled - The server is not operational, usually due to a shutdown/halt request.
•
Suspect - The server may have a problem.
•
Minor - The server encountered a problem that does not seriously affect the HPSS
operation.
•
Major - The server encountered a problem that may seriously impact the overall HPSS
operation.
•
Broken - The server encountered a critical error and shut itself down.
•
Unknown- The server's state is unknown to SSM. SSM should be able to obtain an
Operational State for the server but cannot because SSM cannot communicate with it, and
the server has not set its state to Disabled or Broken. The server may or may not be
running. The reason may simply be that the server is marked executable but is not
running.
•
Invalid - SSM has obtained an Operational State from the server, but its value is not
recognized as a valid one. This may indicate a bug in the server or a communications
problem which is garbling data.
•
None - The server does not have an Operational State (because the server is not
executable, for example), or its Operational State is, by design, unobtainable.
SSM will periodically poll the server’s operational state and update the
Op State
field in the
Servers
window when there are any changes. The rate of the polling is controlled by the SSM
client list refresh rate (see the hpssgui/hpssadm man pages).
Server Name
. The descriptive name of the server.
Host
. The name of the host on which the server is running.
HPSS Management Guide
November 2009
Release 7.3 (Revision 1.0)
85
Summary of Contents for RELEASE 7.3
Page 14: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 14...
Page 195: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 195...
Page 210: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 210...
Page 215: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 215...
Page 222: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 222...
Page 266: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 266...
Page 293: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 293...
Page 367: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 367...
Page 372: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 372...
Page 384: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 384...
Page 388: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 388...