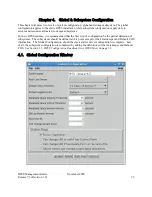
DB Log Monitor Interval.
The Core Server will check consistency of Database Logs and Backup Logs
at the indicated interval, specified in seconds. The logs are consistent if both primary and backup log
directories exist and contain log files with the same names. The minimum value for this field is 300
seconds (5 minutes). A value of 0 will turn off DB Log monitoring. This field may be overridden on the
Storage Subsystem configuration.
COS Change Stream Count.
The number of background threads that run in the Core Server to process
Class of Service change requests. If a value of 0 is specified, the Global Configuration setting will be
used for this storage subsystem.
4.2.3.1. Create Storage Subsystem Metadata
Before creating the subsystem metadata, you must have created the subsystem database that will be used
by the subsystem and have created appropriate tablespaces for the database.
You should review and perform the steps in the following sections in the
HPSS Installation Guide
before
allocating metadata space for the new subsystem:
•
2.3.3
HPSS Storage Subsystems
•
3.5.2
HPSS Infrastructure Storage Space
•
3.5.3
HPSS Filesystems
•
3.5.4
HPSS Metadata Space
•
5.3.2
Install and Configure HPSS – Secondary Subsystem Machine
4.2.3.2. Create Storage Subsystem Configuration
Use the following steps to create a storage subsystem configuration:
1. Decide on a unique descriptive name for the new storage subsystem. SSM will automatically
choose the name “Subsystem #N”, where N is the subsystem ID selected by SSM. The name of
the new storage subsystem may be changed by the administrator at subsystem configuration time
only.
2. From the
Health and Status
window, select Configure/Subsystems from the menu. You will then
be presented a window that lists currently configured subsystems. Select the Create New button to
bring up another window to configure the new subsystem.
3. Enter the name you have chosen for the subsystem in the Subsystem Name field and enter the ID
of the subsystem in the subsystem ID field. Enter the name of the database you have chosen to
contain the tables for this subsystem in the Database Name field.
4. Decide which Classes of Service are to be supported by the new storage subsystem. SSM will
automatically select all Classes of Service to be supported, but the administrator can modify these
choices at any time. Also decide on a default Class of Service for this storage subsystem. By
default SSM leaves this field blank, which means that the default Class of Service specified in the
global configuration will apply to the new storage subsystem as well. The administrator may
choose to override the global value by using the subsystem configuration value at any time.
5. Decide whether gatekeeping or account validation are needed for this storage subsystem. If either
is required, a Gatekeeper will need to be configured for this storage subsystem. If the required
HPSS Management Guide
November 2009
Release 7.3 (Revision 1.0)
79
Summary of Contents for RELEASE 7.3
Page 14: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 14...
Page 195: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 195...
Page 210: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 210...
Page 215: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 215...
Page 222: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 222...
Page 266: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 266...
Page 293: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 293...
Page 367: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 367...
Page 372: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 372...
Page 384: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 384...
Page 388: ...HPSS Management Guide November 2009 Release 7 3 Revision 1 0 388...