FusionModule1000B Air-Cooled IT Solution
Maintenance Guide
3 O&M Description
Issue 02 (2017-01-10)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
13
3.3.6 Emergency Operation
Emergency Operation Description
Emergency operations are performed only when a critical alarm or fault occurs in the
FusionModule1000.
Emergency operations that are included in this manual are common ones for the
FusionModule1000, and may not be inclusive. If a phenomenon or fault is inconsistent
with that described in the emergency operation prerequisites, do not perform operations
based on the method described in this manual.
Emergency operations are basic measures taken to prevent or reduce the loss or
destruction of the FusionModule1000. When performing emergency operations during
the O&M process, take the actual situation into consideration.
Only trained and qualified personnel are allowed to perform emergency operations.
For more emergency operations for the FusionModule1000, contact Huawei technical
support.
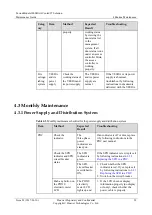
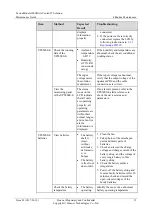
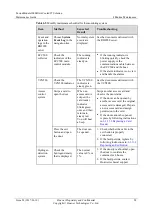
FusionModule1000 Common Critical Alarms and Faults
describes the common critical alarms and faults in the FusionModule1000.
Table 3-2
Common critical alarms and faults
Common Critical
Alarm and Fault
Possible Cause
Possible Impact
Emergency
Operation
The mains supply is
cut off.
The mains supply
is cut off.
Open circuits
occur.
The data center is
powered off.
7.1 Emergency
Operations for
Mains Failure
Circuit breaker
tripping
Overload
protection is
triggered.
Current leakage
protection is
triggered.
Some areas in the
data center are
powered off.
7.2 Emergency
Operations for
Circuit Breaker
Tripping
Overload
The equipment is
overloaded.
The circuit breaker
trips, equipment
deterioration
accelerates, and
even equipment
damage or fire may
occur.
7.3 Overload
Emergency
Operations
Electrolyte leakage
The battery is
damaged.
The battery cannot
work properly.
7.4 Emergency
Operations for
Battery Electrolyte
Leakage
Overtemperature
The cooling
system is set
Equipment
operation is