Chapter 4 System Support
4.4 SYSTEM
RESOURCES
This section describes the availability and basic control of major subsystems, otherwise known as
resource allocation or simply “system resources.” System resources are provided on a priority
basis through hardware interrupts and DMA requests and grants.
4.4.1 INTERRUPTS
The microprocessor uses two types of hardware interrupts; maskable and nonmaskable. A
maskable interrupt can be enabled or disabled within the microprocessor by the use of the STI and
CLI instructions. A nonmaskable interrupt cannot be masked off within the microprocessor,
although it may be inhibited by hardware or software means external to the microprocessor.
4.4.1.1 Maskable
Interrupts
The maskable interrupt is a hardware-generated signal used by peripheral functions within the
system to get the attention of the microprocessor. Peripheral functions produce a unique INTA-H
(PCI) or IRQ0-15 (ISA) signal that is routed to interrupt processing logic that asserts the interrupt
(INTR-) input to the microprocessor. The microprocessor halts execution to determine the source
of the interrupt and then services the peripheral as appropriate.
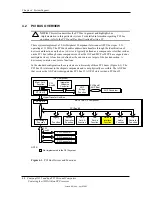
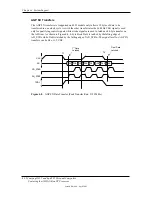
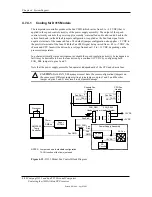
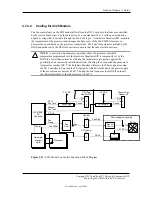
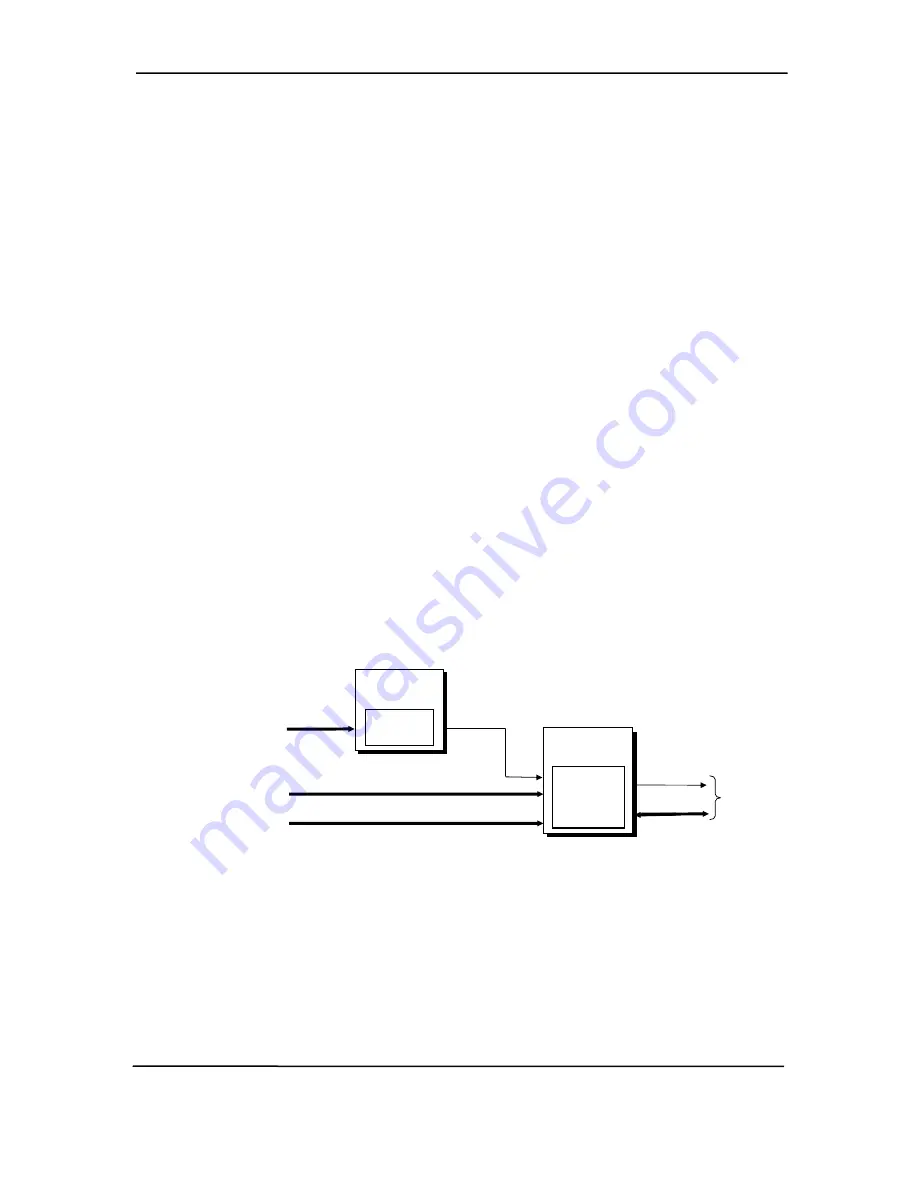
Figure 4-9 shows the routing of PCI and ISA interrupts. Most IRQs are routed through the I/O
controller, which contains a serializing function. A serialized interrupt stream is applied to the
MCP component.
APIC bus
Interrupt
Serializer
LPC47B367
I/O Cntlr.
INTR-
IDE
Hard Drives
IRQ3..7,
9..12,
14,15
INTA-..H-
IRQ14,15
Serial IRQ
Interrupt
Processing
MCP
I/O &
SM Functions
Processor
PCI Peripherals
Figure 4-10.
Maskable
Interrupt Processing, Block Diagram
Interrupts may be processed in one of two modes (selectable through the F10 Setup utility):
♦
8259 mode
♦
APIC mode
Compaq D315 and hp d325 Personal Computers
Featuring the AMD Athlon XP Processor
Second Edition – April 2003
4-14